What is pcba and its components
A Printed Circuit Board Assembly (PCBA) is key to modern electronics. It connects a plain PCB with needed parts to work. PCBA helps improve industries like healthcare and cars. The world PCB market was worth $67.9 billion in 2023. It is expected to grow past $92.4 billion by 2029. This shows the rising need for PCBA in new technology. Companies like LTPCBA offer trusted assembly services with advanced tools, providing high-quality results.
Key Takeaways
PCBA stands for Printed Circuit Board Assembly. It is key for modern electronics, linking parts to make working devices.
Active parts like ICs and transistors improve how devices work. Passive parts like resistors and capacitors keep devices steady.
Checking quality in PCBA making is very important. It includes design reviews, tracking materials, and testing to ensure it works well.
Picking the right assembly method, SMT or THT, depends on the device. SMT works best for small designs, while THT is stronger.
The PCBA market is growing fast worldwide. It is becoming more important in industries like healthcare and cars.
Understanding PCBA
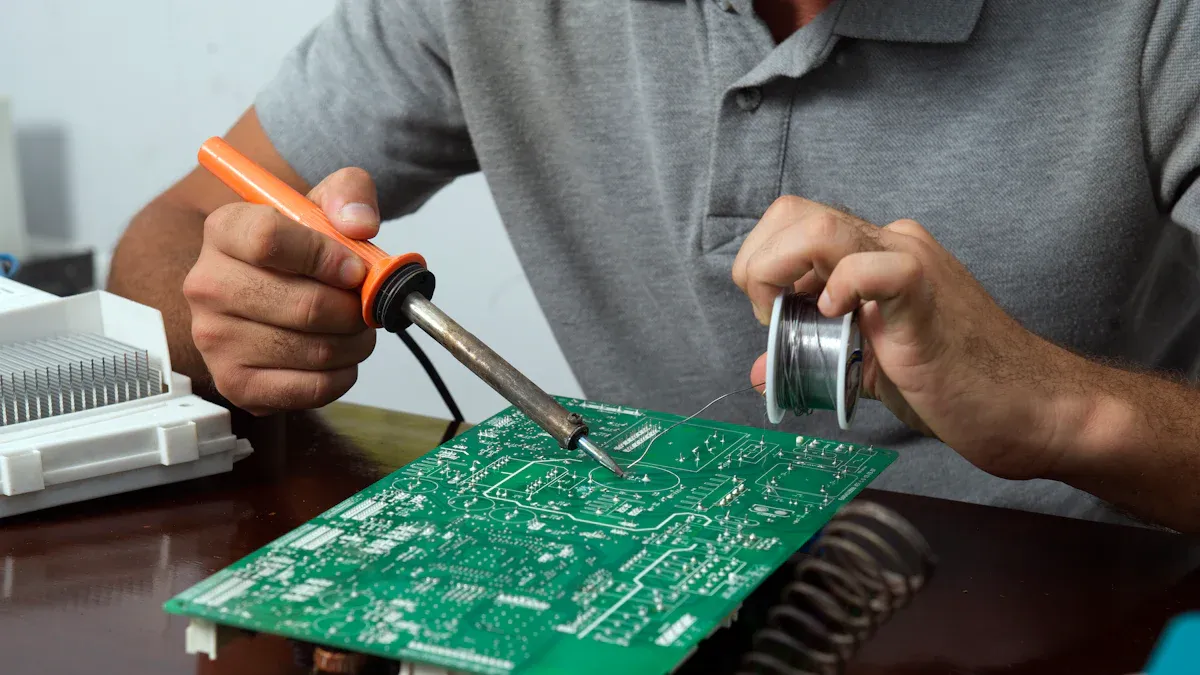

What is PCBA?
PCBA stands for Printed Circuit Board Assembly. It is a PCB with all its parts attached and soldered. This process turns a plain PCB into a working electronic circuit. Active parts like ICs and transistors are added. Passive parts like resistors and capacitors are also included. These parts help the board work in electronic devices.
The PCBA industry follows strict rules to ensure quality. Below is a table of key terms and standards:
Criteria Type | Description |
|---|---|
Standard Definition | |
Accept Criterion | Lists good, okay, and bad conditions for assembly. |
Definition of Defects | Groups defects as critical, major, or minor based on impact. |
Welding Requirements | Explains rules for welding methods and conditions. |
Surface Mount Assembly | Covers adhesive use and part placement in SMT. |
Component Damage | Sets rules for PCB cleanliness, coating, and part safety. |
Discrete Cabling | Details cabling rules without welding and neat wire setup. |
These rules make sure PCBA is reliable and high-quality for different uses.
Why is PCBA essential in electronics?
PCBA is very important in electronics. It connects and powers parts so devices can work. Without PCBA, most electronics would not function. The process ensures parts are placed and soldered correctly. This is key for devices to work well and last long.
Here are reasons why PCBA matters in electronics:
The Physics of Failure method ensures PCBs are reliable and well-made.
Testing and analyzing prototypes confirm PCBs work before use in key systems.
Models check for issues like heat and moisture, ensuring PCBA survives tough conditions.
These steps make PCBA vital in industries needing accuracy and durability.
Common applications of PCBA in various industries
PCBA is used in many industries that depend on electronics. From phones to airplanes, its uses are wide-ranging. The table below shows common PCBA uses in different fields:
Industry | Common Applications |
|---|---|
Mobile Devices | Phones, tablets, GPS devices, alarm clocks |
Computer Electronics | PCs, laptops, monitors, and accessories |
Recording Devices | Cameras, camcorders, microphones |
Entertainment Systems | Game consoles, TVs, DVD players, stereos |
Home Appliances | Microwaves, fridges, coffee makers, alarm clocks |
Industrial Equipment | Drills, presses, measuring tools, power tools |
Automotive | Monitors, control systems, navigation, audio and video devices |
Aerospace | Testing and monitoring tools |
Lighting | LEDs for telecom, cars, computers, medical, and home uses |
These examples show how PCBA helps devices work in daily life and special fields. Whether using a phone or driving, PCBA keeps technology running smoothly.
Key Parts of a PCBA
Active parts (e.g., ICs, transistors)
Active parts are the main pieces of a PCBA. They control electricity flow and do important jobs like boosting signals or switching. Examples include Integrated Circuits (ICs) and transistors. ICs combine many circuits into one chip, making devices smaller and faster. Transistors work as switches or boosters, helping systems run smoothly.
These parts make devices work better. For instance, in gadgets, they speed up processing by 30% compared to older versions. In medical tools, they improve prosthetics' performance. Wearable tech uses them to pack many features into small designs. The table below shows their impact in different areas:
Use | Improvement |
|---|---|
Gadgets | |
Medical Tools | Better prosthetic functions |
Wearable Tech | Combines many features in small designs |
Automation | Boosts reliability and performance |
Passive parts (e.g., resistors, capacitors)
Passive parts don’t make energy but manage and store it. Common ones are resistors, capacitors, and inductors. Resistors control current flow to keep circuits safe. Capacitors store and release energy, helping with filtering and signals. Inductors store energy in magnetic fields, used in tuning and energy storage.
The table below explains their roles and uses:
Part | Job | Examples |
|---|---|---|
Resistor | Controls current flow | Voltage dividers, shunts, buck circuits |
Capacitor | Stores and releases energy | Filtering, signal processing, coupling |
Inductor | Stores energy in magnetic fields | Tuning, filtering, energy storage |
These parts keep PCBA stable and efficient, making them vital for electronics.
Connectors and structural parts
Connectors and structural parts link PCBA to other systems. Connectors move power and signals, while structural parts give support. Their design affects how well the PCBA works.
Important features like current and voltage ratings ensure safety. For example, high current ratings stop overheating, and good signal quality avoids data loss. The table below highlights their importance:
Feature | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
Current Rating | Stops overheating, prevents failures |
Voltage Rating | Handles voltage safely, avoids breakdowns |
Signal Quality | Keeps signals clear in fast systems |
Contact Resistance | Less resistance means better performance |
Durability | Important for parts used often |
Material Strength | Protects against damage from the environment |
Shape and Size | Affects layout and compatibility |
Temperature Range | Works well in different temperatures |
Safety Standards | Meets rules for safety and eco-friendliness |
These parts ensure strong connections and support, helping PCBA work perfectly.
Specialized components (e.g., sensors, LEDs)
Specialized parts like sensors and LEDs make a PCBA better. They give devices extra features, making them smarter and more useful.
Light-Emitting Diodes (LEDs) are small lights used in many devices. They glow when electricity flows through them the right way. You can find LEDs in displays, indicators, and lights. They save energy and last a long time, which is great for modern gadgets. To work safely, LEDs need a resistor to limit current. This stops too much electricity from damaging them. For example, traffic lights and digital signs use LEDs with resistors to work well.
Sensors are also important in PCBA. They sense things like motion, heat, or light and turn these into signals. Other parts on the board use these signals to work. Sensors are used in things like smart lights, air monitors, and temperature trackers. For instance, a motion sensor in a smart home turns on lights when someone enters a room. In medical tools, temperature sensors check a patient’s condition.
These parts make devices work better and add cool features. Adding sensors and LEDs to a PCBA helps create smart electronics for many industries, like healthcare and home gadgets.
Tip: Pick the right sensors and LEDs for your project. This helps your PCBA work well and last longer.
PCBA Manufacturing Process
PCB design and fabrication
The success of a PCBA starts with its design and making. A good PCB design helps lower costs, speeds up assembly, and makes it more reliable. Following smart design steps can make the process smoother and improve how it works.
Smart Component Placement: Place parts close together to save time during assembly. This makes production faster and more efficient.
Clear Labels: Use easy-to-read labels to help identify parts quickly. This speeds up checking and reduces mistakes.
Standardized Sizes: Use the same part sizes across products. This saves money by reusing tools and machines.
Pay attention to design details that affect how well the PCB works and how easy it is to make. The table below shows some important tips:
Best Practice | What It Means | Why It Helps |
|---|---|---|
Part Spacing | Leave enough room between parts | Avoids problems during assembly |
Trace Width | Use proper widths for currents | Stops overheating and signal loss |
Via Placement | Keep vias out of fast paths | Keeps signals clear |
Panelization | Group boards for easy assembly | Saves material and lowers costs |
Solder Mask | Leave space for solder | Prevents solder from connecting wrongly |
By designing your PCB carefully, you can make production easier and ensure the final product works well.
Tip: Avoid sharp turns in traces and limit vias in fast paths to keep signals strong.
Component placement and soldering
After making the PCB, the next step is adding parts and soldering them. This turns the PCB into a working PCBA. Parts must be placed correctly, and soldering must be done well for the board to work properly.
Placing Parts: Machines place parts on the PCB with great accuracy. Placing them smartly avoids problems and makes the process faster.
Soldering: Soldering connects parts to the PCB. It melts solder to create strong electrical and physical bonds. Two common methods are reflow soldering (for surface parts) and wave soldering (for through-hole parts).
Good soldering is very important. Bad soldering can cause weak connections, leading to device failures.
Note: Always check solder joints for problems like cold joints or solder bridges to ensure quality.
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) vs. Through-Hole Technology (THT)
When building a PCBA, you can choose between Surface Mount Technology (SMT) and Through-Hole Technology (THT). Each has its own strengths and is best for certain uses.
The table below compares these two methods:
Through Hole Benefits | |
|---|---|
Parts can go on both sides of the PCB. | Handles bigger, stronger parts like power supplies. |
Smaller and lighter parts. | Makes stronger connections. |
Fits more parts in less space. | Handles physical stress better. |
Fewer holes needed in the PCB. | Great for parts like switches that need handling. |
Less manual work during production. | Works well in tough environments. |
More automated placement and soldering. | Easier to fix by hand if needed. |
Better electrical performance. | Good for high-power parts. |
Lowers production costs. | Some parts only come in through-hole form. |
SMT is best for small, high-tech designs, while THT works better for strong, durable parts. Knowing the benefits of each helps you pick the right method for your project.
Tip: Use SMT for modern, lightweight gadgets and THT for parts that need extra strength or frequent use.
Inspection and quality control steps
Checking and controlling quality is very important for a PCBA. Finding problems early saves money and ensures high-quality products. Here are the main steps in the quality control process:
Early Design Check: Look at the design before making the product. This helps find and fix problems early, making production easier.
Careful Material Handling: Use parts from trusted suppliers and track them closely. This keeps the materials stable and reliable.
Step-by-Step Monitoring: Watch every part of the process to keep it consistent and error-free.
Double Testing: Test the PCBA in different conditions to make sure it works well.
Ongoing Improvements: Use feedback from checks to make the process better over time.
Careful inspection makes sure every PCBA works without problems. This step is key to keeping products reliable and working well. Fixing issues early helps products last longer and protects your brand's image.
Note: Strong quality checks not only improve products but also make customers happier by giving them dependable electronics.
LTPCBA’s advanced manufacturing capabilities
LTPCBA is a leader in making advanced PCBA assemblies. They handle tricky parts like BGA (Ball Grid Array) components, which are important for modern devices. Here’s how LTPCBA compares to older SMT methods:
Feature | LTPCBA (BGA Assembly) | Traditional SMT Packages |
|---|---|---|
Cost | Lower assembly cost | Higher assembly cost |
Alignment | Aligns itself during reflow | Needs manual alignment |
Size | Smaller and thinner | Bigger and thicker |
Heat Control | Easier heat and current control | Harder to manage heat |
Wiring | Simpler wiring | More complex wiring |
Connection Density | Higher connection density | Lower connection density |
LTPCBA works with all kinds of BGAs, from tiny ones (2mm x 3mm) to large ones (45mm). They can also place parts with very small gaps (0.25mm), ensuring accuracy in every build.
LTPCBA also focuses on strong solder connections. They carefully choose pad types, sizes, and surface treatments for the best results. This attention to detail ensures every PCBA meets top quality and reliability standards.
Tip: Picking a skilled manufacturer like LTPCBA can make your PCBA last longer and work better.
Differences Between PCBA and PCB
What is a PCB?
A Printed Circuit Board (PCB) is the base of electronic devices. It is a flat board made from materials like fiberglass. Thin copper layers are added to create paths, called traces, that connect parts of a circuit. A PCB holds and links components but cannot work on its own. Think of it as a blank sheet ready to be turned into something useful.
PCBs are used early in designing electronics. Engineers test and check circuits on them before adding parts. Without PCBs, making small and reliable devices would be very hard.
How PCBA builds upon PCB
A PCBA turns a PCB into a working circuit. This is done by attaching parts like resistors, capacitors, and chips to the board. These parts are placed and soldered using methods like Surface Mount Technology (SMT) or Through-Hole Technology (THT).
A PCBA is the final version that powers devices. While a PCB is just the base, a PCBA makes things like phones, computers, or car systems work. The assembly process ensures all parts are in the right place and connected properly, making the PCB fully functional.
Key differences in functionality and manufacturing
The main differences between a PCB and a PCBA are in their purpose, look, and how they are made. The table below shows these differences:
Aspect | PCB (Printed Circuit Board) | PCBA (Printed Circuit Board Assembly) |
|---|---|---|
Definition | Empty board with electrical paths | Board with parts attached, forming a working circuit |
Function | Supports and connects parts | Performs specific electronic tasks |
Components | None (just the board) | Includes resistors, capacitors, chips, etc. |
Appearance | Flat board with tracks, pads, and holes | Board with many parts attached |
Manufacturing | Adding copper layers and solder mask | Placing and soldering parts onto the board |
Testing | Checks for proper connections | Full testing to ensure it works |
Stage | Starting point | Finished, working circuit |
Applications | Used for testing and designing circuits | Found in final products like phones and computers |
Knowing these differences helps you see how both are important. A PCB is the base, while a PCBA is the finished product that powers your devices.
PCBA is crucial for modern electronics. It turns a plain PCB into a working circuit. Active parts like ICs and transistors, along with passive parts like resistors and capacitors, help devices work smoothly. Special parts, such as sensors and LEDs, add smart features to electronics.
Making PCBA requires careful steps, like placing parts and soldering them. Quality checks, like automated inspections and testing, ensure the boards are reliable. The global PCBA market is growing fast, from $68.4 billion in 2023 to $105.8 billion by 2032. This shows how important PCBA is becoming.
For reliable PCBA services, LTPCBA provides advanced solutions. Their skills ensure top-quality assemblies made to fit your needs. They are a trusted name in the industry.
FAQ
What is the difference between SMT and THT in PCBA?
SMT puts parts directly on the PCB surface. It works well for small designs. THT places parts through holes in the PCB. This makes connections stronger. Use SMT for light gadgets and THT for tough devices.
Tip: Mix both methods for flexible designs.
How do you ensure PCBA quality?
Quality is ensured by careful checks and tests. Design reviews catch early mistakes. Materials are tracked to keep them reliable. Automated tests check for errors. Testing in different conditions ensures the PCBA works well. Pick manufacturers with strong quality controls.
Note: LTPCBA uses advanced tools to keep high standards.
Why is PCBA important in electronics?
PCBA links and powers parts so devices can work. Without it, electronics like phones wouldn’t function. It places and solders parts correctly. This improves how devices perform and last.
Can PCBA be customized for specific needs?
Yes, PCBA can be made to fit special needs. You can choose parts, layouts, and features for your project. Companies like LTPCBA offer flexible options for prototypes and production.
What industries benefit most from PCBA?
Many industries depend on PCBA for their devices. Healthcare uses it for medical tools. Cars rely on it for navigation systems. Aerospace needs it for testing tools. Electronics use it for phones and gadgets.
Emoji Insight: 🏥 Healthcare, 🚗 Cars, ✈️ Planes, 📱 Gadgets.
See Also
Exploring Comprehensive Turn-Key Solutions for PCB Assembly
A Guide to SMT and DIP Assembly in PCBA
The Role of Industrial Serial Screen PCBA Today
Essential Criteria for PCB Boards in SMT Processes
Boosting Project Efficiency with Rapid PCB Assembly Prototypes
