What You Need to Know About Wave Soldering Principles in SMT

Wave soldering joins electronic parts to printed circuit boards. It does this by moving them over a wave of melted solder. This step is very important in surface mount technology assembly. Many electronics makers like wave soldering. Automation, robots, and AI help make it more exact and faster.
The market for wave soldering fluxes is getting bigger. This is because more people want consumer electronics, electric vehicles, and telecommunications.
New trends like making things smaller and complex board designs need careful control of soldering quality.
Key Takeaways
Wave soldering uses melted solder in a wave shape. It joins electronic parts to PCBs. This makes strong connections. It works well for through-hole components.
LTPCBA uses a careful wave soldering process. They use modern machines. They check quality at every step. This helps make sure results are good and reliable.
You pick wave soldering or reflow soldering based on the parts and board design. LTPCBA uses both ways. This helps give the best solution for each project.
Wave Soldering Basics
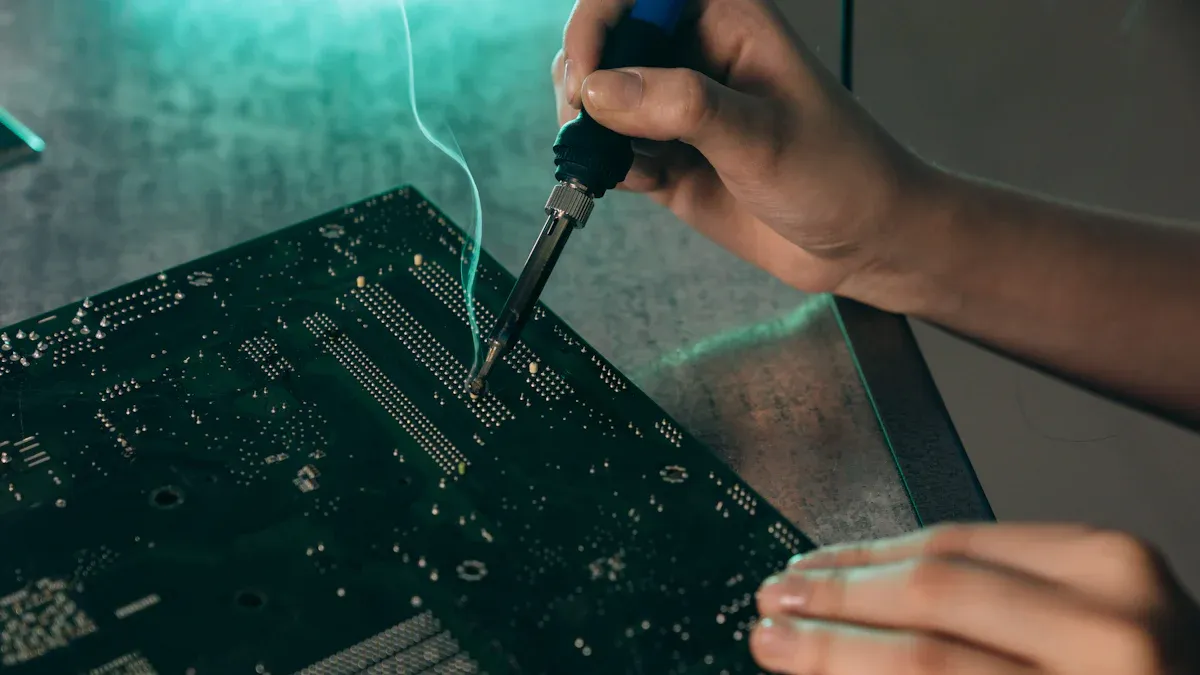
What Is Wave Soldering
Wave soldering joins electronic parts to a PCB using melted solder. The machine makes a wave with pumps or nitrogen. The PCB moves over the wave. The solder connects metal pads and leads. This process is used a lot in making electronics, cars, and medical devices. The table below shows how wave soldering is different from other ways:
Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
Principle | Uses hot liquid tin to solder parts by touching them directly. |
Equipment | Has spray, preheating, tin furnace for the wave, and cooling. |
Process Steps | Includes spraying flux, preheating, soldering, and cooling. |
Types | Lead, lead-free, and nitrogen wave soldering. |
Differences from Reflow | Uses melted solder wave for plug-in parts; reflow melts solder paste for SMT. |
Applications | Used a lot in electronics, cars, and medical products. |
Technical Details | Makes a solder wave crest with pumps or nitrogen; joins parts as PCB goes through the wave. |
How It Works in SMT
Wave soldering moves a PCB with parts through melted solder. A pump in the tank makes the wave. The PCB goes through at a set angle and depth. The solder touches the metal pads and leads. This makes strong solder joints. In SMT, wave soldering is used for boards with both surface mount and through-hole parts.
Key Principles
Wave soldering is best for through-hole parts but can do some surface mount parts with care.
Preheating the PCB from both sides helps stop cold solder joints.
Surface tension and atomic forces help solder stick to pads and leads.
Cleaning oxides off metal is needed for good solder flow.
The speed the PCB leaves the wave changes how solder drains and the joint quality.
The shape and place of leads can change how solder spreads and if problems happen.
Tip: Keeping the right heat and using flux helps stop cracks or holes in solder joints.
Wave Soldering Process with LTPCBA
Step-by-Step Process
LTPCBA uses a careful wave soldering process. This helps make sure the results are good. The process has several main steps:
Fixture Installation
Technicians put the PCB on a fixture. The fixture keeps the board flat. This stops it from bending when heated. Flat boards are important, especially if they are thin.Flux Coating
A machine sprays flux on the PCB. Flux cleans off oxides from metal. It also stops new oxides from forming. Flux makes the solder spread better. LTPCBA checks air pressure and flux levels. This keeps the coating even.Preheating
The PCB goes through a preheating area. The heat makes the flux solvent go away slowly. This lowers stress on the board. LTPCBA sets the heat between 90°C and 130°C. The board stays there for 1 to 3 minutes. This step helps stop solder splashes. It also protects the parts on the board.Soldering
The PCB moves over melted solder. The angle and depth are set carefully. LTPCBA keeps the solder at about 275°C. The conveyor moves at about 1300 cm/min. These settings help the solder flow well. This makes strong solder joints.Cooling
The board cools down after soldering. Cooling makes the solder joints hard and strong.
Note: LTPCBA checks each step with strict quality rules. They watch solder temperature, conveyor speed, flux amount, and PCB quality. This careful checking helps stop problems like weak solder joints or parts falling off.
Equipment and Technology
LTPCBA uses modern machines for wave soldering. The company buys equipment that helps make fewer mistakes. The table below lists some main machines and what they do:
Equipment/Technology | Technical Feature/Specification | Role in Wave Soldering Process |
|---|---|---|
Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) | Finds defects automatically | Checks solder joints for errors |
X-ray Inspection System | Micro-focus, 3D tomography | Detects hidden solder problems |
Solder Paste Printer + SPI | Ultra-fine pitch, ±15μm accuracy, real-time 3D inspection | Ensures even solder paste application |
SMT First Article Inspection Machine | AI vision, flying probe, <0.1% error rate | Compares BOM to PCB, boosts inspection speed |
DIP Production Line | Chain/rotary conveyance, auto-insertion, wave soldering for through-hole components | Supports reliable soldering for large parts |
LTPCBA also uses reflow ovens with exact temperature control. They use fast pick-and-place machines too. These tools help keep the process steady. They also help with making complex boards.
Advantages and Disadvantages
LTPCBA’s wave soldering process has many good points:
High Reliability: The process makes strong joints, especially for through-hole parts.
Advanced Quality Assurance: LTPCBA uses AOI, X-ray, ICT, FCT, and flying probe tests. These tests find problems early and make sure each board is good.
International Standards: The company follows ISO, IATF, and UL rules. This makes sure the boards are safe and high quality.
Customer Support: LTPCBA gives fast quotes and 24-hour tech help. Customers get help at every step.
Efficient Production: Automated lines and careful controls make work fast and steady.
There are some challenges, like needing skilled workers and being sensitive to the environment. But LTPCBA’s team and machines help handle these issues.
Tip: Picking LTPCBA means you get new technology and strong quality checks for wave soldering jobs.
Wave Soldering vs Reflow Soldering
Wave soldering and reflow soldering are used for different jobs in electronics. The table below shows how the two methods compare:
Aspect | Wave Soldering | Reflow Soldering |
|---|---|---|
Component Compatibility | Best for surface-mount parts (SMT) | |
Solder Temperature | About 250-270°C | Peak about 220-250°C |
Process Steps | Flux spraying, pre-heating, wave contact, cooling | Solder paste application, thermal profile, cooling |
Production Efficiency | Batch process, conveyor speed 0.5-2.5 m/min | Continuous, good for high-density SMT |
Quality & Reliability | Strong joints, risk of bridging if uncontrolled | Consistent joints, fewer voids and tombstoning |
Equipment Complexity | Needs expert operation, complex wave control | Easier to control, advanced ovens available |
Environmental Factors | Sensitive to changes in temperature and humidity | More stable, controlled atmosphere possible |
Wave soldering uses a wave of melted solder to join parts. Reflow soldering melts solder paste with controlled heat. Wave soldering needs careful control of flux, heat, and timing. Reflow soldering is easier to automate for small parts and crowded boards. LTPCBA uses both ways and picks the best one for each job.
Wave soldering joins electronic parts to PCBs in SMT. LTPCBA uses new machines and checks quality well. People should think about what they need, the tools, and the rules before picking a company.
LTPCBA gives good results for many kinds of businesses.
FAQ
What types of PCBs work best with wave soldering?
Wave soldering works best with through-hole PCBs. Mixed-technology boards with both through-hole and some surface-mount parts also fit this process.
How does LTPCBA ensure quality in wave soldering?
LTPCBA uses AOI, X-ray, and strict process controls. Technicians check every step. The company follows ISO, IATF, and UL standards.
Tip: LTPCBA’s team answers questions quickly. Customers can get support 24 hours a day.
Can wave soldering handle lead-free requirements?
Yes. LTPCBA uses both leaded and lead-free solder. The company meets RoHS and other environmental standards.
See Also
Comprehensive Instructions For Wave Soldering In SMT Assembly
Essential Criteria For Wave Soldering In DIP Assembly
Common Causes Of Component Detachment During SMT Wave Soldering
Key Process Standards For Reflow Soldering In SMT Production
Top SMT Assembly Techniques For Superior Electronic Manufacturing
