SMT PCB Assembly vs. Through-Hole Technology: Which Is Right for Your Electronics Project?
When choosing SMT PCB Assembly or Through-Hole Technology, think about size, strength, and price. Surface mount technology works well for small designs like gadgets. Through-hole parts are stronger and better for tough conditions. Making through-hole boards needs more work, which costs more and slows production.
Key Takeaways
SMT PCB Assembly works well for small and light designs. It is great for fast production, like in phones or smartwatches.
Through-Hole Technology gives strong connections, good for high-power uses. It works well in places with heat or shaking.
You can mix SMT and Through-Hole methods for some projects. This is helpful when you need both small size and strength.
Understanding SMT PCB Assembly and Through-Hole Technology

What Is SMT PCB Assembly?
Surface mount technology (SMT) is a way to attach parts to a circuit board. Instead of putting parts through holes, they are placed on top of the board. This method makes designs smaller, lighter, and more compact. It’s great for things like phones, laptops, and smartwatches.
Machines are used to place parts quickly and accurately. These machines can handle thousands of parts in an hour. This speeds up production and lowers costs. Smaller parts and less solder are needed, saving money. SMT is a smart choice for making many products fast.
To keep quality high, SMT follows strict rules. For example:
Standard | What It Covers |
|---|---|
Rules for solder joints and placing parts. | |
IPC J-STD-001 | Focuses on soldering and keeping boards clean. |
IPC-7351 | Gives tips for designing board patterns for better soldering. |
IPC-7711/7721 | Explains how to fix or rework electronic boards. |
SMT is also very reliable. The soldering process helps prevent part failures. This ensures the product lasts longer. Because of this, SMT is popular in industries needing precision and speed.
What Is Through-Hole Technology?
Through-hole technology is an older way to build circuit boards. It involves putting part leads through holes in the board. These leads are soldered on the other side. This creates strong connections, making it good for tough conditions.
Through-hole parts are bigger than SMT parts, so they’re easier to handle. This is helpful for beginners or projects done by hand. The strong connections make it great for places with heat or vibrations.
Here are some benefits:
Advantage/Use | Details |
|---|---|
Reliability | Strong and dependable, perfect for important projects. |
Mechanical Strength | Leads make sturdy connections that resist stress. |
Works in Tough Conditions | Handles heat, humidity, and other hard environments well. |
Easy to Use | Bigger parts are simpler to handle and solder by hand. |
Applications | Used in aerospace, military, and school projects. |
But through-hole has downsides. Fewer parts fit on the board because it’s less compact. It also takes longer to make since more work is done by hand. Even with these issues, through-hole is still a good choice for strong and durable projects.
Comparing the Pros and Cons of SMT and Through-Hole
Advantages of SMT PCB Assembly
SMT has many benefits for modern electronics.
Compact Designs: SMT fits more parts on smaller boards. This is great for devices like phones and smartwatches.
Faster Assembly: Machines place thousands of parts quickly, speeding up production.
Cost Efficiency: Smaller parts and less solder lower material costs.
High Volume Production: SMT works well for making many products at once.
Here’s a simple look at SMT benefits:
Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
Component Density | Fits more parts for smaller designs. |
Assembly Speed | Faster production with automated machines. |
Cost Efficiency | Saves money on materials and labor. |
Application Suitability | Best for making large amounts of products. |
SMT is perfect for projects needing small, lightweight designs.
Disadvantages of SMT PCB Assembly
SMT also has some downsides to think about.
Reliability Concerns: Small parts can break easily in tough conditions.
Heat Dissipation Issues: SMT struggles with high-power parts because of heat problems.
Initial Setup Costs: SMT machines are costly, which may not suit small projects.
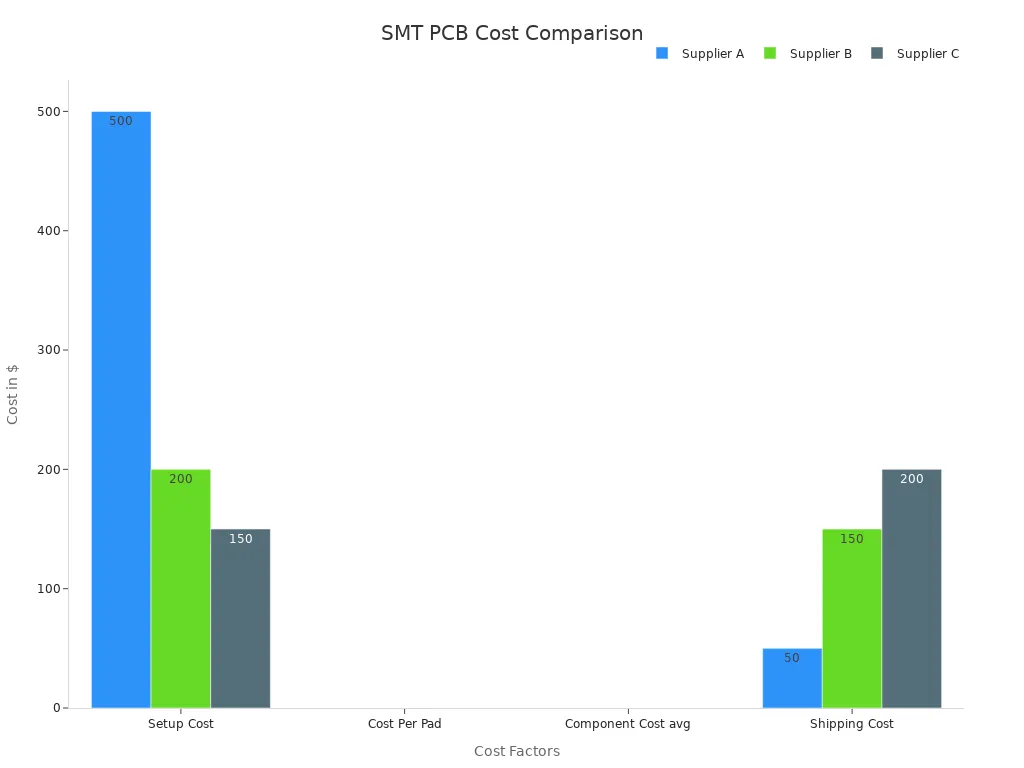
Here’s an example of setup costs for SMT:
Factor | Supplier A (Domestic) | Supplier B (International) | Supplier C (International) |
|---|---|---|---|
Setup Cost | $500 | $200 | $150 |
Cost Per Pad | $0.015 | $0.008 | $0.006 |
Component Cost | $0.10 | $0.08 | $0.09 |
Shipping Cost | $50 | $150 | $200 |
Lead Time | 2 weeks | 4 weeks | 3 weeks |
While SMT is fast and efficient, these issues might affect your project if durability or cost matters most.
Advantages of Through-Hole Technology
Through-hole assembly is strong and reliable for certain projects.
Mechanical Strength: Parts soldered through holes are strong and resist stress.
High Power Handling: Through-hole parts handle heat better, great for high-power uses.
Ease of Repair: Testing and fixing through-hole parts is easier.
Reliability: Often used in important products like military and aerospace equipment.
Here’s a breakdown of its strengths:
Performance Metric | Description |
|---|---|
Strong connections resist physical stress. | |
High Power Handling | Handles heat well for powerful parts. |
Ease of Testing and Repair | Easier to fix and replace parts. |
Reliability | Works well under tough conditions. |
Thermal Performance | Better at managing heat. |
Vibration and Shock Resistance | Stays strong in shaky or rough environments. |
Through-hole is a good choice for projects needing strength and durability.
Disadvantages of Through-Hole Technology
Through-hole assembly also has some drawbacks.
Larger Board Sizes: Bigger parts take up more space on the board.
Slower Assembly Speeds: Manual soldering takes more time.
Higher Labor Costs: More handwork means higher costs.
Here’s a comparison of SMT and through-hole assembly:
Feature | SMT Limitations | THT Advantages | THT Limitations | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Component Density | Fits more parts on smaller boards | Small parts may break easily | Strong connections | Takes up more space |
Board Size | Smaller boards | Struggles with heat for powerful parts | Handles heat better | Needs larger boards |
Assembly Speed | Faster with machines | Expensive setup costs | Strong solder joints | Slower manual assembly |
Cost Efficiency | Saves space and materials | N/A | N/A | Costs more due to manual work |
Application Suitability | Great for mass production | N/A | Good for tough environments | N/A |
Through-hole may not be best for small or fast projects, but it’s great for reliable and strong designs.
Key Factors to Think About When Picking the Right Technology
Component Density and Size
When making a PCB, think about how many parts can fit. This is called component density. SMT uses smaller parts and places them on both sides of the board. This makes it great for small devices like phones. Through-hole uses bigger parts, which lowers density but makes repairs easier.
To design well, focus on standardizing part sizes. This helps parts work together and lowers costs. Also, leave space around parts for easy checking and fixing.
Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
Board Density | Fits more parts in layers or keeps designs simple. |
Footprint Standardization | Matches part sizes to cut costs and reuse tools. |
Accessibility | Leaves space for easy checking and fixing. |
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Strength matters for electronics facing stress, heat, or shaking. Through-hole is better here because its parts are soldered through the board. This makes them stronger and less likely to break. It’s great for tough jobs like in planes or military gear.
Tests show strong parts make products last longer. Early testing and changes can improve strength. If your project needs to handle tough conditions, through-hole is the best choice.
Study Focus | Key Findings |
|---|---|
Mechanical Loads | Looked at how parts handle stress and wear. |
Failure Modes | Studied how and why parts fail during use. |
Product Robustness | Used testing and changes to make products stronger. |
Cost and Budget Limits
Your budget is important when picking a method. Through-hole is simpler and cheaper for small projects. SMT costs less for making many items because it’s faster. But complex designs with SMT and multilayer boards cost more due to special tools and skills needed.
Simple projects cost less with through-hole assembly.
Complex SMT designs with many layers cost more due to tools and expertise.
Assembly Speed and Production Volume
For making many products fast, SMT is the best. SMT machines can place 25,000 parts per hour. A line with four machines can place 100,000 parts per hour. This speed is much faster than manual through-hole assembly. For big projects, SMT saves time and boosts efficiency.
SMT machines place 25,000 parts per hour.
Four SMT machines can place 100,000 parts per hour.
SMT is much faster than manual methods.
Environmental and Operating Conditions
Where your electronics will be used affects your choice. Through-hole works better in tough places like high heat, humidity, or shaking. Tests like constant temperature and humidity checks ensure PCBs can handle these stresses. SMT is efficient but less reliable in harsh conditions.
Environmental tests mimic real-life conditions like heat, humidity, and shaking.
Constant temperature and humidity tests check PCB quality for tough environments.
The Role of Reliability in PCB Assembly
How SMT PCB Assembly Ensures Reliability
SMT PCB assembly improves reliability using advanced tools and strict rules. Machines like pick-and-place systems and inspection tools place parts accurately. This lowers mistakes and boosts how well electronics work. Good stencil designs and careful solder paste use are also important. These steps fix up to 75% of common problems, making strong solder joints and reducing errors.
Manufacturers follow strict rules to keep quality high. Tests for heat and stress find weak spots early. Fixing these issues ensures products work well in different conditions. Smart machines also help build complex PCBs faster and better, improving reliability even more.
Key Factors in SMT Reliability | Benefits |
|---|---|
Advanced Machinery | Accurate and quick assembly |
Quality Standards | Fewer mistakes during production |
Smart Automation | Better performance for complex boards |
When Through-Hole Technology Offers Greater Reliability
Through-hole technology is more reliable in certain cases. It’s great for parts that face physical stress. The soldered leads make strong connections, perfect for high-power and high-voltage needs.
This method works well in tough environments too. For example, medical tools and aerospace devices often use through-hole because it lasts under extreme conditions. Tests like heat cycling and vibration checks prove its strength in these situations.
Mechanical Strength: Handles physical stress well.
High-Power Applications: Works with high currents and voltages.
Harsh Environments: Stays reliable in tough conditions.
Choosing through-hole for these uses ensures your electronics stay strong and dependable, even in hard situations.
Can Both SMT and Through-Hole Be Used Together?

What Is Hybrid PCB Assembly?
Hybrid PCB assembly uses both SMT and through-hole methods on one board. This combines the best of both technologies for better designs. SMT parts are small and lightweight, while through-hole parts are strong and durable.
Hybrid boards are made to work well and save energy. Each layer can be set up for tasks like power or heat control. This makes hybrid assembly great for complex projects like medical tools, airplanes, and everyday electronics.
Feature | Advantage |
|---|---|
Signal Clarity | Keeps signals clean and free from noise |
Heat Control | Helps parts stay cool and last longer |
Uses fewer expensive materials | |
Component Mixing | Combines different parts effectively |
When to Use a Hybrid Approach
Hybrid assembly is useful when you need small designs and strong parts. SMT works for packed circuits, while through-hole handles high power and stress well.
Testing helps decide if hybrid assembly is needed. Electrical tests check signals, while mechanical tests look at strength. Environmental tests mimic real-world conditions to ensure reliability. A Taiwan company showed how hybrid assembly helps adapt to changing needs. This makes it a smart choice for flexible production.
Electrical tests check signal quality and circuit performance.
Mechanical tests measure strength under bending or pressure.
Environmental tests simulate heat, cold, and other conditions.
How LTPCBA Supports Hybrid PCB Assembly Solutions
LTPCBA is skilled in hybrid PCB assembly for many industries. They use advanced tools to mix SMT and through-hole parts smoothly. This ensures reliable and high-quality products.
For radar systems, LTPCBA improves signal clarity and heat control. In medical tools, they help make small, wearable devices. Aerospace projects benefit from boards that fit tight spaces but stay strong. Consumer electronics gain sleek designs with LTPCBA’s expertise.
Industry | Contribution |
|---|---|
Radar Systems | Improves signals and controls heat |
Medical Devices | Creates small, wearable monitors |
Aerospace Projects | Builds strong boards for tight spaces |
Consumer Electronics | Designs stylish and efficient gadgets |
By combining SMT and through-hole, LTPCBA creates hybrid solutions for modern electronics.
Picking SMT or THT depends on your project’s needs. SMT works well for small designs and fast production. THT is better for tough conditions and strong connections. Use SMT for gadgets like phones. Choose THT for durable parts in rough environments. LTPCBA provides quality assembly for both methods and hybrid boards.
FAQ
1. Can you use both SMT and Through-Hole Technology on the same PCB?
Yes, hybrid PCB assembly uses both SMT and through-hole parts. This method combines small designs with strong connections for flexible uses.
Tip: Pick hybrid assembly for projects needing strength and many parts.
2. Which technology is better for high-power applications?
Through-hole technology is best for high-power devices. Its soldered leads manage heat and stress well, making it great for powerful electronics.
3. How do you decide between SMT and Through-Hole for your project?
Think about your project’s needs. Use SMT for small designs and fast production. Choose through-hole for strong parts and tough conditions.
Note: Check your budget and where the device will be used before choosing.
See Also
When Traditional PCB Assembly Surpasses Modern SMT Techniques
Evaluating Reliability Between Through Hole and SMT Assembly
Exploring Advantages and Disadvantages of SMD and Through-Hole
Selecting the Best Through Hole PCB Assembly for Industry Use
Ultimate Resource for Understanding Through Hole PCB Assembly
