10 Must-Know Quality Control Practices for Professional Through Hole PCB Assembly
Professional circuit board assembly needs careful quality checks at every step. Important steps include design review, checking parts, PCB board inspection, lead preparation, soldering process control, solder joint quality control, visual and AOI inspection, electrical testing, advanced quality checkpoints, and packaging. LTPCBA is very good at quality assurance for through hole pcb assembly and professional pcb assembly. They follow top industry standards and rules:
Testing Method | Quality Metrics / Benchmarks |
|---|---|
In-Circuit Testing (ICT) | Finds up to 90% of defects, covers up to 90% of faults, finds about 30% of common PCB problems |
Functional Testing | Checks repeatability, reliability, traceability, diagnostics, and keeps watching |
Automated Optical Inspection | Gives 100% accuracy, 18% fewer false alarms, finds problems early |
X-ray Inspection | Finds hidden solder problems, uses 2D and 3D analysis |
Burn-In Testing | Makes sure boards last long under tough conditions |
LTPCBA’s careful circuit board assembly sets a high standard for quality in pcb production.
Key Takeaways
Careful quality checks happen at each step. This starts with design review and ends with final packaging. These checks help make strong and reliable through hole PCB assemblies. They also make sure the assemblies meet industry standards.
Advanced inspection tools are used. These include Automated Optical Inspection, X-ray, and electrical testing. These tools help find hidden problems early. This lowers mistakes and makes the product better.
Detailed records are kept during the whole process. Clear communication is also important. These things help solve problems quickly. They also help track parts and keep quality high.
Design Review
DFM Checks
Design for Manufacturability (DFM) checks are very important in making circuit boards. The design team should do these checks early. They should not wait for the manufacturer to do them. A DFM checklist helps find problems before they get expensive. This list looks at things like what materials to use, how close parts are, steps to put it together, and what tests are needed.
Working together with designers, customers, and manufacturers helps everyone see problems and lowers risks.
A DFM scorecard shows how easy the design is to make.
ISO 9001:2015 says teams must keep records of design reviews and changes. This helps track what happens and keeps things under control. By following these rules, teams can match their pcb designs with quality systems.
Risk Reduction
A good design review helps lower risks at every step of making a pcb. Through-hole technology gives strong support and can handle a lot of power. This makes it good for tough jobs. It is important to control hole sizes for strong boards and good solder joints. Teams should use normal hole sizes, keep enough space, and write down each step.
Manual assembly lets people check and fix things closely.
Quality control means checking sizes, materials, and doing electrical tests.
Talking openly between designers and manufacturers helps control sizes and stop mistakes.
Testing like visual checks, AOI, and in-circuit testing make sure the circuit board is good. These steps help every pcb meet industry rules and work well in real life.
Component Inspection
Visual Checks
Visual checks are very important in through hole PCB assembly. Skilled workers look at boards to find problems like solder bridging or missing parts. They use tools that make things look bigger. They also check design papers to make sure everything is right. Workers do these checks many times during production. This helps them find problems early.
Automated Optical Inspection uses cameras and lights to look at boards fast. AOI systems, such as the MIRTEC MV-3L, can find tiny problems. These machines help stop mistakes people might miss. 3D AOI can measure how high and big parts and solder joints are. This helps find even more problems. These checks make sure every board is high quality.
Measurable Result / Benefit | Description | Example Application / Outcome |
|---|---|---|
Finds surface problems and mistakes early in production. | Stops bad boards from moving forward or going to customers. | |
Increased Production Speed & Accuracy | Machines check for errors fast and cut down on waste. | Helps make more boards and earn more money in big factories. |
Improved Product Quality and Safety | Watching boards all the time makes sure they have no problems. | Used to check car and airplane parts. |
ESD Protection
Electrostatic discharge can hurt electronic parts during assembly. Workers wear special clothes and use wrist straps that are grounded. Work tables have ESD mats and ionizers to keep static away. Good ESD protection keeps parts safe and makes the final product work well. People check ESD controls often to make sure they work. LTPCBA always follows strong ESD rules to keep every board safe.
PCB Board Inspection
Surface Quality
Surface quality is very important in pcb assembly. Teams use special tools to check each pcb’s surface. Automated Optical Inspection uses cameras and lasers to spot problems. It can find missing parts and bad solder joints. Three-Dimensional AOI also measures how tall things are on the board. This gives a better look at the whole surface. Automated X-ray Inspection finds hidden cracks or solder problems inside the board. Solder Paste Inspection checks if the right amount of solder paste is in the right place. These tools help teams find problems early and keep boards good.
Note: Many companies use First Article Inspection to make sure the first pcb in a batch is correct. Certifications like ISO 9001:2015 and ISO 13485:2016 show the inspection follows strict rules. Military and defense jobs may need MIL-PRF-31032 or DLA approval. This proves the highest level of quality control.
AOI and AXI find both surface and hidden problems.
SPI checks if solder paste is used the right way.
FAI and certifications show the process is always the same.
Continuity Testing
Continuity testing checks if the pcb’s electrical paths work right. Technicians use special tools to send signals through the board. If the signal does not go through, there is a break or short. This step helps find open circuits or wrong connections before moving on. Good continuity testing makes sure every board is safe and works well.
Lead Preparation
Cutting and Bending
Getting leads ready is very important in through hole PCB assembly. Workers cut each lead to the right length before putting it in the board. They use special tools so the lead fits the hole and is not too long. Bending the lead at the right angle helps hold the part in place. Workers follow rules so they do not make sharp bends. Sharp bends can make the metal weak. They use jigs or forming tools to make every bend the same. This makes sure each part sits flat and does not move during soldering.
Tip: Cutting and bending leads the same way every time helps make better boards and means less fixing later.
Damage Prevention
Keeping leads safe from damage is very important for good assembly. Workers are careful so they do not scratch, nick, or break the leads. They do not push too hard when putting leads into the PCB. Using the right tools stops the leads from getting crushed or bent wrong. Workers check each lead for damage before going to the next step. They keep parts in safe boxes until they need them. Being careful keeps the work easy and stops problems that cost money later.
Use ESD-safe tools to touch leads.
Check leads before and after putting them in.
Keep parts in anti-static boxes.
Careful lead work helps make strong boards that last a long time.
Soldering Process Control
Method Selection
Picking the right soldering method is very important. Technicians choose hand soldering, wave soldering, or selective soldering. The choice depends on the board’s design and where parts are placed. Each method is good for different jobs. Hand soldering is best for small batches or test boards. Wave soldering is used for making many boards at once. Selective soldering works for tricky boards with special spots.
Teams check many things to make sure the job is done well:
Visual checks look for good wetting, the right fillet size, and no cracks or holes.
Technicians make sure the solder material is correct and stored right.
They check the type of alloy and flux, and look at shelf life.
They watch the temperature closely, making sure it heats and cools just right.
Cleanliness checks make sure nothing dirty is left on the board.
Teams follow lead-free rules and care about the environment.
They test if solder joints are strong enough to handle stress.
Tip: Picking the best method and checking quality stops mistakes and makes boards work better.
Process Monitoring
Process monitoring helps the assembly line work well. It makes sure every board meets high standards. Teams use SPC and control charts to watch for changes in soldering. They figure out the Cp to see if the process stays in the right range.
Finding defects helps spot problems like solder bridging or not enough solder. Teams use root cause analysis, like the 5 Whys or fishbone diagrams, to fix problems fast. Checks like visual inspection, X-ray, and AOI help find defects early and keep the quality high.
Solder Joint Quality Control

IPC Standards
Checking solder joints is a big part of quality control. People use IPC standards to know what a good solder joint looks like. These rules, like IPC-A-610, say joints should look smooth and shiny. The fillet angle must be between 90° and 120°. This helps make the joint strong and reliable. The table below shows how different IPC classes change the rules and how many mistakes are allowed:
IPC Class | Description | Quality and Testing Requirements | Defect Tolerance and Reliability Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
Class 1 | Consumer electronics (e.g., toys) | Basic functionality focus; relaxed tolerances | Up to 10% defect allowance; minimal testing |
Class 2 | Extended life electronics (e.g., laptops) | Stricter inspections; balance of cost and performance | Defect tolerance reduced to 5% for critical features |
Class 3 | High-reliability electronics (e.g., medical, aerospace) | 100% inspection and testing; zero defects allowed | Ensures performance in demanding environments; critical safety |
LTPCBA always follows these IPC rules. The company trains workers with special CIS and CIT programs. This training helps everyone spot problems and keep quality high. LTPCBA has a 99.5% pass rate. This shows they care about doing a good job.
Defect Detection
Finding defects early is very important for quality. LTPCBA uses special tools like X-ray, AOI, and electrical tests to find bad solder joints. These tools help catch more problems and make fewer mistakes. The chart below shows that using more than one test helps find more defects:
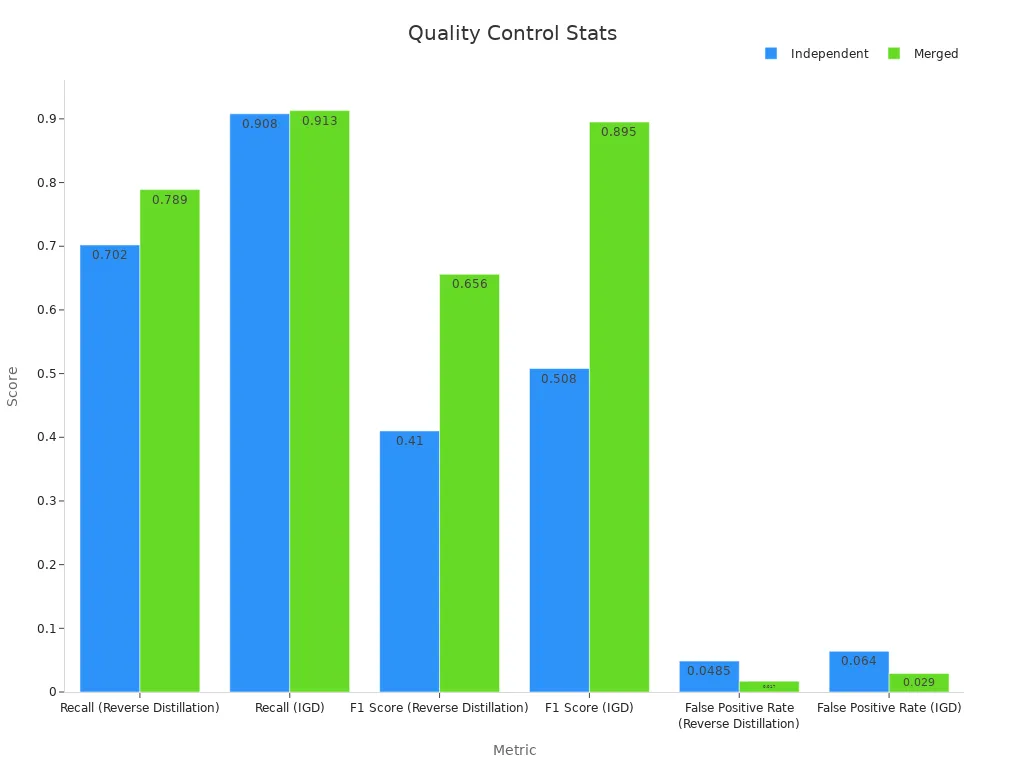
Technicians use both non-destructive and destructive tests. Non-destructive tests include X-ray and dye tests. Destructive tests, like micro-sectioning, help look at defects closely. Electrical and environmental tests check if boards work under stress. These steps make sure every board is safe and high quality.
Visual and AOI Inspection
Manual Checks
Manual checks are very important for checking through hole PCB assembly. Skilled workers use magnifying lamps and microscopes to look at the boards. They search for problems like solder bridges, missing parts, or parts that are not lined up. Each board gets close attention from the workers. They look at the board and compare it to pictures and papers. If they find a problem, they mark it so it can be fixed. This step helps find mistakes early before the boards move on.
Note: Manual checks give fast feedback and let workers fix things right away. They also help teach new workers what to look for during assembly.
Automated Optical Inspection
Automated optical inspection uses special cameras and computer programs to check each board. The system looks for problems like parts in the wrong place, bad solder joints, or missing parts. It can check many boards quickly and does not make many mistakes. The machine compares each board to a digital picture. If it finds something different, it sends an alert for someone to check. This way of checking helps stop human mistakes and makes work faster.
Inspection Method | Strengths | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|
Manual Checks | Flexible, detailed, immediate | Small batches, prototypes |
Automated Optical Inspection | Fast, consistent, high-volume | Mass production |
Both manual and automated checks help make sure every board is good. LTPCBA uses both ways to get great results for every job.
Electrical Testing
Electrical testing is very important in through hole PCB assembly. It helps teams find problems that eyes cannot see. There are two main ways to test: in-circuit test (ICT) and functional testing.
ICT
In-circuit test uses a bed-of-nails fixture. This tool touches many spots on the board at once. It checks each part and connection quickly. ICT finds open circuits, shorts, and wrong parts. Guarding techniques help test each part by itself. Teams use ICT a lot in big factories. It gives fast and trusted results. For example, SMT Corp found half of three-phase bridge rectifiers failed electrical tests. These parts looked fine in visual checks. This means ICT can find problems that other checks miss. ICT also gives data to help control the process. It helps teams get more good boards the first time.
Functional Testing
Functional testing checks if the board works as it should. Teams turn on the board and run test signals. This step acts like real use. It helps find bad connections or parts in the wrong place. The table below shows how different tests help during making boards:
Test Type | Fault Detected | Impact on Product | Outcome / Efficiency Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
Continuity Test | Open circuit in trace | Device won’t power on | Fault detected, board rewired |
Solder Joint Check | Cold solder joint | Poor connection | Reflow soldering fixes the issue |
Functional Test | Faulty connections | Delays during inspection | Faster assembly line turnaround |
Automated test equipment makes functional testing quick and correct. Real-time data from these tests helps teams fix problems fast. Electrical testing makes sure every board is good before it ships.
Advanced Quality Control Checkpoints
Advanced quality control checkpoints are very important for making sure through hole pcb assembly is reliable. LTPCBA uses special inspection tools to meet tough rules and make boards last a long time. These checkpoints help teams find hidden issues and make the boards better.
X-ray Inspection
X-ray inspection is a strong tool for checking quality. It finds problems inside the board that people cannot see. These problems include voids, cracks, and parts that do not line up right in solder joints. X-ray machines give clear 2D and 3D pictures, so teams can look at every layer closely. Automation lets X-ray checks happen fast and saves data, which helps keep boards safe. This test does not hurt the board, so it stays whole. LTPCBA uses X-ray inspection to find hidden problems and make sure boards work well for tough jobs.
Finds inside problems like voids, cracks, and misalignments
Gives clear 2D and 3D pictures for close checks
Lets teams watch and save data as they check
Does not damage the board during testing
Lowers mistakes and keeps quality the same
Environmental Testing
Environmental testing is another big part of quality control checkpoints. This test checks how boards work when they get hot, cold, or shake. It helps teams know if boards will last a long time and work well. Industry rules say teams must use careful ways to test and get good data. LTPCBA uses tests like heating, cooling, and shaking to act like real life. These checkpoints help teams find weak spots and make every board stronger.
Note: LTPCBA’s advanced checkpoints, like X-ray and environmental testing, help make through hole pcb assembly very reliable.
Documentation and Traceability
Record Keeping
Good record keeping is very important for quality control in through hole PCB assembly. Teams use the same document style with headers and footers. They keep track of which version is the newest. Only approved documents are used to make boards. Signatures show who checked and allowed each document. Teams make records as they work, so everything can be traced.
Being open and able to trace actions means everyone can see what happens. Audit trails and tracking tools watch for changes, deletions, and approvals. Each action has a name and time, so you know who did what and when.
Some best ways to do this are:
Use version control so old info is not used.
Control who can see or change important data.
Make sure documents go to the right people.
Check and review documents often.
A digital system helps teams find and protect documents fast. Leaders tell everyone what is expected and give the tools needed. They make sure everyone is responsible for their work. Teams check how correct and fast their records are, and look at audit results to see how well they are doing.
Process Tracking
Process tracking lets teams watch every step of PCB assembly. If there is a problem, they can look back and find out why. Traceability data helps teams find slow steps and fix them.
Value stream mapping uses traceability to show each step, how much material is used, and how long each step takes.
New audit software and AI tools make tracking easier and more correct.
Work in progress tracking watches materials as boards are made, so teams can fix problems fast.
Shipment history connects lot codes to orders and shipments, so teams can recall products quickly if needed.
A connected database keeps all the data from making, storing, and checking boards in one place. This makes it easy to trace boards, check audits, and follow rules. Real-time data shows where products are and how they move. Teams can act fast, keep the company’s good name, and stop mistakes.
Packaging and Shipping
Protective Packaging
Protective packaging is very important for professional pcb assembly. LTPCBA uses special packaging to keep boards safe from bumps and shakes. The team picks materials and designs that follow industry rules like ASTM D-4169 and D-5276. These rules help test how packaging handles drops, shakes, and heavy weight. Machines like vibration tables and shock testers check if the packaging can protect the boards. Compression tests see if boxes can handle being stacked in warehouses or trucks. Distribution tests give repeatable results to show if the packaging stays strong during shipping. LTPCBA looks at these test results to find weak spots and make packaging better. This way, every board arrives safe and ready to use.
Note: Good packaging not only keeps products safe but also helps save money and the environment.
Final Quality Checks
Final quality checks are the last step before shipping in professional pcb assembly. LTPCBA’s team checks each order to make sure it is right and complete. They use warehouse systems and barcode scanners to track every board. The company has an order accuracy rate higher than 98%. This shows they work hard to do a great job. Perfect orders and on-time shipping prove that shipments go out as promised. Extra services like kitting and testing before shipping make quality even better. Big warehouses and good locations help stop mistakes and get orders out fast. LTPCBA’s careful work means customers always get good boards on time.
Using all 10 quality control practices helps make PCBs very reliable. LTPCBA uses these steps and gets great results. They have a 99.5% pass rate and happy customers. Their careful checks and controls help make boards that last a long time.
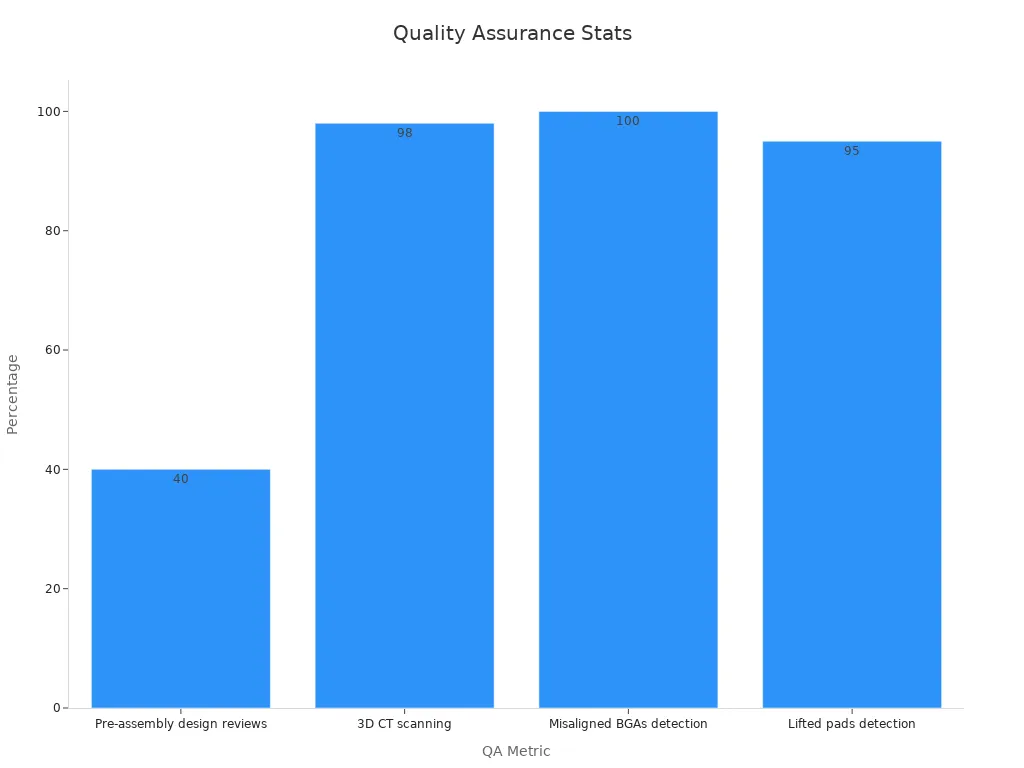
Quality Assurance Metric | Description | Statistic/Value |
|---|---|---|
Pre-assembly design reviews | Finds design problems early and lowers risks | |
X-ray inspection | Finds hidden problems inside the boards | 3–5% of boards checked have defects |
3D CT scanning | Finds empty spots in solder | 98% of empty spots are found |
Misaligned BGAs detection | Finds open circuits | 100% of these problems are found |
Lifted pads detection | Finds loose connections | 95% of these problems are found |
FAQ
What makes LTPCBA’s quality control different?
LTPCBA uses special inspection tools and follows strict rules. The team checks each board at every step. This way, every PCB assembly is high quality.
How does LTPCBA handle traceability?
LTPCBA keeps digital records for every board. The system saves each step and who did it. This helps the team find and fix problems fast.
Why is X-ray inspection important in through hole PCB assembly?
X-ray inspection finds hidden problems inside solder joints. It helps teams see things that eyes might miss. This step makes boards work better and last longer.
See Also
Essential Quality Control Steps For Through Hole PCB Assembly
Top Five Testing Techniques For Through Hole PCB Assembly
Complete Handbook For Effective Through Hole PCB Assembly
SMT Assembly Techniques To Ensure Superior Electronic Production
Steps To Guarantee Perfect BGA Assembly Through Quality Checks
