How Medical PCBA Prototypes Achieve Quality and Safety
Quality and safety are paramount in the field of medical devices, where both patients and healthcare professionals depend on flawless performance. Every prototype PCBA medical solution is subjected to stringent testing and inspection, as precision is critical in medical applications. Choosing a certified contract manufacturer is essential to guarantee that each prototype PCBA medical device meets the highest standards of performance and reliability. Hospitals and clinics consistently trust certified contract manufacturers to provide dependable prototype PCBA medical assembly services for their vital equipment.
Key Takeaways
Medical PCBA prototypes must follow strict international standards like ISO 13485, IPC Class 3, and FDA regulations to ensure safety and reliability.
Choosing a certified manufacturer like LTPCBA guarantees high-quality assembly through advanced testing, cleanroom environments, and detailed documentation.
Careful design and material selection, including biocompatible components, help prevent device failures and support patient safety.
Thorough testing methods such as AOI, X-ray inspection, and environmental stress tests catch defects early and confirm long-term performance.
Continuous risk management and regular compliance audits keep medical PCBA prototypes safe, reliable, and ready for real-world medical use.
Standards and Regulations
Medical printed circuit boards must comply with a complex framework of standards and regulations to ensure patient safety and device reliability. These regulatory standards guide every stage of design, manufacturing, and testing. The following sections outline the most important guidelines and how leading manufacturers like LTPCBA demonstrate best practices in compliance.
ISO 13485 and ISO 9001
ISO 13485 and ISO 9001 form the foundation of quality management for medical printed circuit boards. ISO 13485 certification focuses on regulatory standards specific to medical devices, requiring strict documentation, risk management, and traceability. Manufacturers must maintain detailed records of every material, process, and test. This approach supports rapid investigations and corrective actions if issues arise. ISO 9001 provides a broader framework for process control and continual improvement, serving as the base for ISO standards in many industries.
ISO 13485 certification demands proactive risk management tools such as Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) and Fault Tree Analysis (FTA). These tools help identify and reduce potential failures before they reach patients. The standard also requires management to assign clear roles and responsibilities for regulatory compliance. In contrast, ISO 9001 emphasizes customer satisfaction and process improvement across all industries.
ISO 9001 | ISO 13485 | |
|---|---|---|
Scope | General quality management system | Medical device manufacturing with regulatory focus |
Regulatory Compliance | Not specifically enforced | Strict enforcement for medical devices |
Risk Management | Broad | Focused on medical device lifecycle |
Documentation | Flexible | Strict, detailed, no deviations |
Management Responsibility | Flexible | Designated roles for QMS and compliance |
Traceability | Not emphasized | Paramount for each unit |
Focus | Customer satisfaction | Safety, effectiveness, compliance |
LTPCBA demonstrates compliance with both ISO 13485 and ISO 9001, ensuring that every medical PCB assembly meets global safety standards and regulatory standards.
IPC-A-610, IPC-6012, and IPC-A-600
IPC standards provide essential guidelines for the design, fabrication, and assembly of medical printed circuit boards. These guidelines classify products into three classes, with Class 3 reserved for high-performance electronics such as medical devices. IPC-A-600 focuses on the visual and structural acceptability of bare boards, while IPC-6012 sets performance and qualification requirements for rigid PCBs. IPC-A-610 addresses the acceptability of assembled PCBs, emphasizing soldering quality and assembly workmanship.
Focus Area | Acceptance Criteria Highlights | |
|---|---|---|
IPC-A-600 | Visual and structural acceptability | Uniform plating, no cracks, complete solder mask, no internal defects |
IPC-6012 | Performance and qualification | Dielectric/conductor specs, plating, cleanliness, thermal stress, reliability |
IPC-A-610 | Acceptability of assemblies | Soldering quality, component mounting, Class 3 standards for medical devices |
Manufacturers use these guidelines to ensure that medical printed circuit boards meet the highest reliability and safety requirements. LTPCBA follows IPC standards rigorously, applying Class 3 acceptance criteria to every medical PCB assembly.
IPC standards standardize manufacturing, minimize errors, and ensure consistent quality.
Class 3 IPC standards are essential for life-support and other critical medical applications.
Adherence to these guidelines reduces defects, rework, and recalls, supporting regulatory standards and patient safety.
FDA 21 CFR Part 820 and UL
FDA 21 CFR Part 820 outlines the regulatory standards for medical device manufacturing in the United States. These guidelines require manufacturers to establish comprehensive quality systems, implement design controls, and maintain strict documentation. Key requirements include:
Executive management responsibility and personnel training
Design controls for input, review, validation, and verification
Environmental and contamination controls
Rigorous document control and change management
Production and process controls, including equipment maintenance and calibration
Corrective and preventive action (CAPA) systems
Handling, storage, and distribution procedures
Comprehensive records, including Device Master Record (DMR) and Device History Record (DHR)
Accurate labeling and packaging
Servicing procedures and documentation
Statistical techniques for inspection and validation
UL standards further enhance the safety profile of medical printed circuit boards. UL certification, including UL 796 and UL 94, ensures that PCBs meet strict electrical, mechanical, and flammability requirements. The certification process includes design review, prototype testing, manufacturing audits, and ongoing compliance checks. UL standards guarantee material quality, construction integrity, and fire resistance, which are critical for medical applications.
UL standards require manufacturers to use recognized materials and optimize design parameters for safety.
The UL mark signifies compliance with global safety standards and regulatory standards, providing a competitive advantage and building trust with customers.
LTPCBA maintains UL certification, demonstrating a commitment to safety and reliability in every medical PCB assembly.
IEC 60601, IPC-2221, ASME V&V 40
IEC 60601 sets the global safety standards for medical electrical equipment, including medical printed circuit boards. This standard addresses safety, electromagnetic compatibility, and device functionality. Manufacturers must ensure that every device meets these guidelines to protect patients and healthcare professionals.
IPC-2221 provides general guidelines for PCB design, including layout, materials, and EMI standards. These guidelines help manufacturers control electromagnetic interference and ensure signal integrity in medical devices. EMI standards are especially important for devices used in sensitive environments such as hospitals.
ASME V&V 40 offers guidelines for verification and validation of medical devices. These regulatory standards require manufacturers to test and validate every device under real-world conditions, ensuring that it performs safely and effectively.
LTPCBA demonstrates compliance with IEC 60601, IPC-2221, and ASME V&V 40, using advanced inspection technologies and rigorous testing protocols.
The company operates cleanrooms and uses 3D AOI and X-ray systems to verify solder joint quality and layer alignment.
LTPCBA’s commitment to these guidelines ensures that every medical PCB assembly meets or exceeds global safety standards.
Manufacturers must follow all relevant standards and regulations to ensure the safety, reliability, and effectiveness of medical printed circuit boards. LTPCBA’s adherence to ISO standards, UL standards, IPC standards, and other regulatory standards sets a benchmark for quality in the industry.
Prototype PCBA Medical Design
Medtech PCB Design Principles
Medtech pcb design begins with strict adherence to regulatory guidelines. Engineers must follow standards such as FDA, ISO 13485, and IEC 60601 to ensure patient safety and device reliability. Key principles include careful component placement, optimized signal routing, and robust power and ground plane design. Miniaturization plays a major role in modern medical devices, requiring high-density layouts and advanced techniques like microvias and 3D pcb prototyping. Cleanroom environments and ESD protection are essential for medical pcb assembly. LTPCBA uses advanced BGA assembly and high-precision drilling to meet the demands of prototype pcba medical projects. Their automated inspection systems, including AOI and X-ray, help maintain high performance and quality.
Material and Component Selection
Material selection directly impacts the safety and performance of prototype pcba medical solutions. Substrates such as FR-4, polyimide, and ceramic offer different benefits for medical pcb design. For wearable or implantable medical devices, biocompatibility is critical. Components must resist corrosion and tolerate sterilization. LTPCBA sources components that comply with RoHS and ISO 10993, ensuring safe operation in healthcare pcbs. Protective coatings and sterilization-ready materials further enhance reliability. Early selection of biocompatible materials reduces the risk of costly redesigns and regulatory delays in medical device manufacturing.
Traceability and Documentation
Traceability forms the backbone of quality assurance in medical device pcb assemblies. Every step in pcb assembly, from material sourcing to final inspection, must be documented. LTPCBA maintains a centralized database for all process data, including supplier codes, inspection results, and operator records. Barcode scanning and serial numbers allow quick identification of printed circuit board assemblies. Detailed inspection reports and compliance certifications support regulatory audits. This level of documentation ensures that prototype pcba medical products meet industry guidelines and pass all required tests.
Risk Management
Risk management is integrated throughout the medtech pcb design process. Engineers use hazard analysis tools like FMEA and fault tree analysis to identify and control potential hazards. ISO 13485 and IEC 60601 require ongoing risk assessment, control implementation, and validation testing. LTPCBA harmonizes these standards with FDA regulations to strengthen risk management in every prototype pcba medical project. Their approach includes continuous monitoring and improvement, ensuring that medical technology boards remain safe and reliable. Effective risk management reduces the chance of device failure and supports long-term patient safety.
LTPCBA’s commitment to advanced technology, strict documentation, and comprehensive risk management sets a high standard for pcb prototyping in medical devices. Their expertise as a certified contract manufacturer ensures that every pcb assembly meets the rigorous demands of the healthcare industry.
Testing and Validation
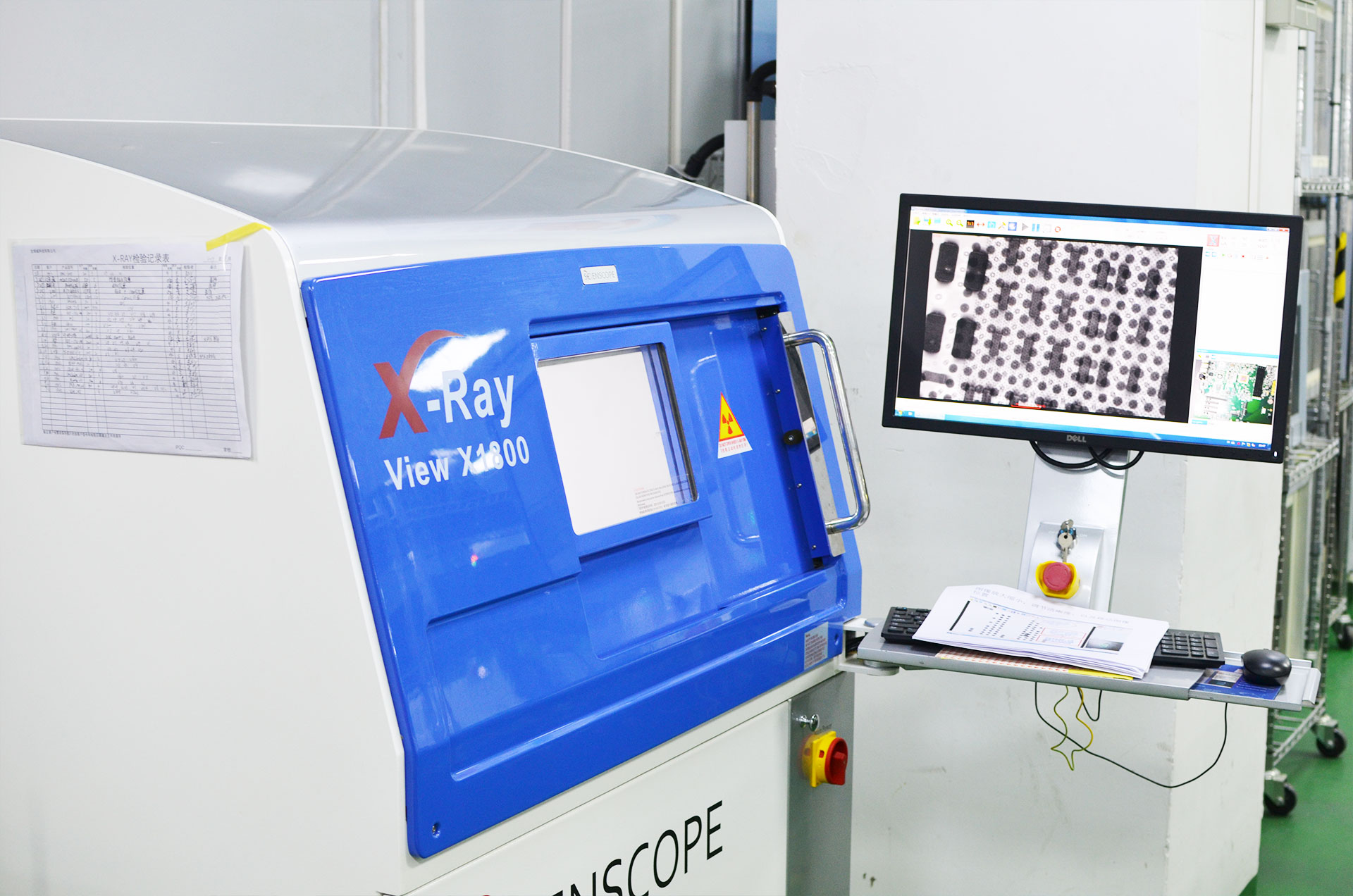

Testing and validation play a vital role in ensuring the reliability and safety of medical device pcb assemblies. Manufacturers must conduct a series of safety and performance tests to meet international standards and regulatory requirements. These steps confirm that every prototype can withstand real-world conditions and deliver consistent performance in critical healthcare environments.
Functional and Environmental Testing
Medical device pcb assemblies undergo a range of functional and environmental tests. These tests verify that each assembly meets strict performance criteria and can operate safely in demanding medical settings. The following table summarizes the most important testing types:
Testing Type | Description | Purpose/Regulatory Relevance |
|---|---|---|
In-Circuit Testing (ICT) | Electrical testing of components and connections after assembly | Ensures correct placement and soldering integrity |
Functional Circuit Testing (FCT) | Verifies overall performance in operational conditions | Confirms device meets performance requirements |
Aging Tests | Prolonged operation or stress to identify early failures | Ensures long-term reliability and durability |
Thermal Cycling | Repeated temperature changes | Tests resistance to temperature extremes |
Environmental Stress Testing | Simulates harsh conditions, including temperature and mechanical stress | Ensures reliability and safety under expected scenarios |
Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) | Visual inspection for soldering defects and component placement | Detects manufacturing defects to maintain quality |
LTPCBA uses advanced AOI systems before and after soldering. These systems detect defects early, reducing rework and improving overall performance. 3D AOI technology measures solder joint height and component alignment, which is critical for medical applications. X-ray inspection and in-circuit testing further enhance defect detection, ensuring assemblies meet the highest standards.
Verification and Validation (V&V)
Verification and validation activities confirm that medical device pcb assemblies meet all design and regulatory requirements. Manufacturers follow protocols such as design verification testing, system integration validation, and usability assessments. These steps cover functional, environmental, safety, and reliability aspects. Documentation includes detailed reports, traceability matrices, and technical files. Design reviews involve cross-functional teams to ensure objectivity and completeness. LTPCBA maintains comprehensive records, supporting regulatory submissions and continuous improvement.
Verification checks that the design meets specified requirements.
Validation ensures the final product performs as intended in real-world use.
Traceability links every test result to design inputs and risk controls.
Accelerated life testing and stress testing, such as HALT, expose prototypes to extreme conditions. These tests reveal weaknesses and help engineers improve design and materials, increasing confidence in long-term performance.
Compliance Audits
Compliance audits ensure ongoing adherence to standards and regulations. Auditors review supplier certifications, process documentation, and risk management frameworks. Regular audits verify that manufacturers maintain corrective and preventive actions, lot traceability, and complete records. LTPCBA undergoes frequent internal and external audits to maintain ISO 13485 and IPC Class 3 certifications. These audits identify gaps, support continuous training, and help manufacturers adapt to regulatory changes. Consistent compliance audits protect patient safety and guarantee that medical device pcb assemblies remain reliable throughout their lifecycle.
Regular testing, validation, and audits form the backbone of quality assurance for medical device pcb assemblies. LTPCBA’s multi-layered approach, combining AOI, X-ray, and functional testing, ensures every product meets strict safety and performance tests required in the medical industry.
Adhering to rigorous regulatory standards ensures medical devices deliver reliable performance and protect patient safety.
Quality management systems and continuous risk assessment help identify hazards and improve outcomes for every device.
Robust design, manufacturing, and validation processes guarantee that medical devices meet strict requirements.
Partnering with experienced providers like LTPCBA increases the success rate of prototype PCBA medical projects.
Teams should always prioritize best practices and compliance in medtech PCB design to support safe, effective device innovation.
FAQ
What makes medical PCBA prototypes different from standard PCB assemblies?
Medical PCBA prototypes require strict adherence to international standards. They must pass rigorous testing for safety, reliability, and biocompatibility. Manufacturers like LTPCBA use advanced inspection systems and maintain detailed documentation to meet these higher requirements.
Why is traceability important in medical device PCB assemblies?
Traceability allows manufacturers to track every component and process step. This ensures quick identification of issues, supports regulatory audits, and helps maintain patient safety. LTPCBA uses barcode scanning and centralized databases for complete traceability.
How does LTPCBA ensure compliance with global standards?
LTPCBA follows ISO 13485, ISO 9001, IPC Class 3, and UL standards. The company uses automated inspection, cleanroom assembly, and regular audits. These practices guarantee that every medical printed circuit board meets or exceeds international requirements.
What types of testing do medical PCBA prototypes undergo?
Medical PCBA prototypes undergo functional, environmental, and reliability tests. These include in-circuit testing, AOI, X-ray inspection, and thermal cycling. Each test checks for defects, durability, and performance under real-world conditions.
Can LTPCBA handle urgent prototype PCBA medical projects?
Yes. LTPCBA offers quick response services, including fast quotations and 24-hour technical support. The company’s advanced technology and efficient processes help deliver urgent medical PCBA prototypes on time.
See Also
Essential PCBA Processing Standards For Medical Device Manufacturing
Ways Modern Turnkey PCBA Plants Guarantee High Quality Output
Critical Methods To Enhance PCBA Durability And Performance
The Role Of X-Ray Inspection In PCBA Quality Assurance
Understanding PCBA And Its Essential Component Parts Explained
