What Does PCBA Mean in Electronics Manufacturing
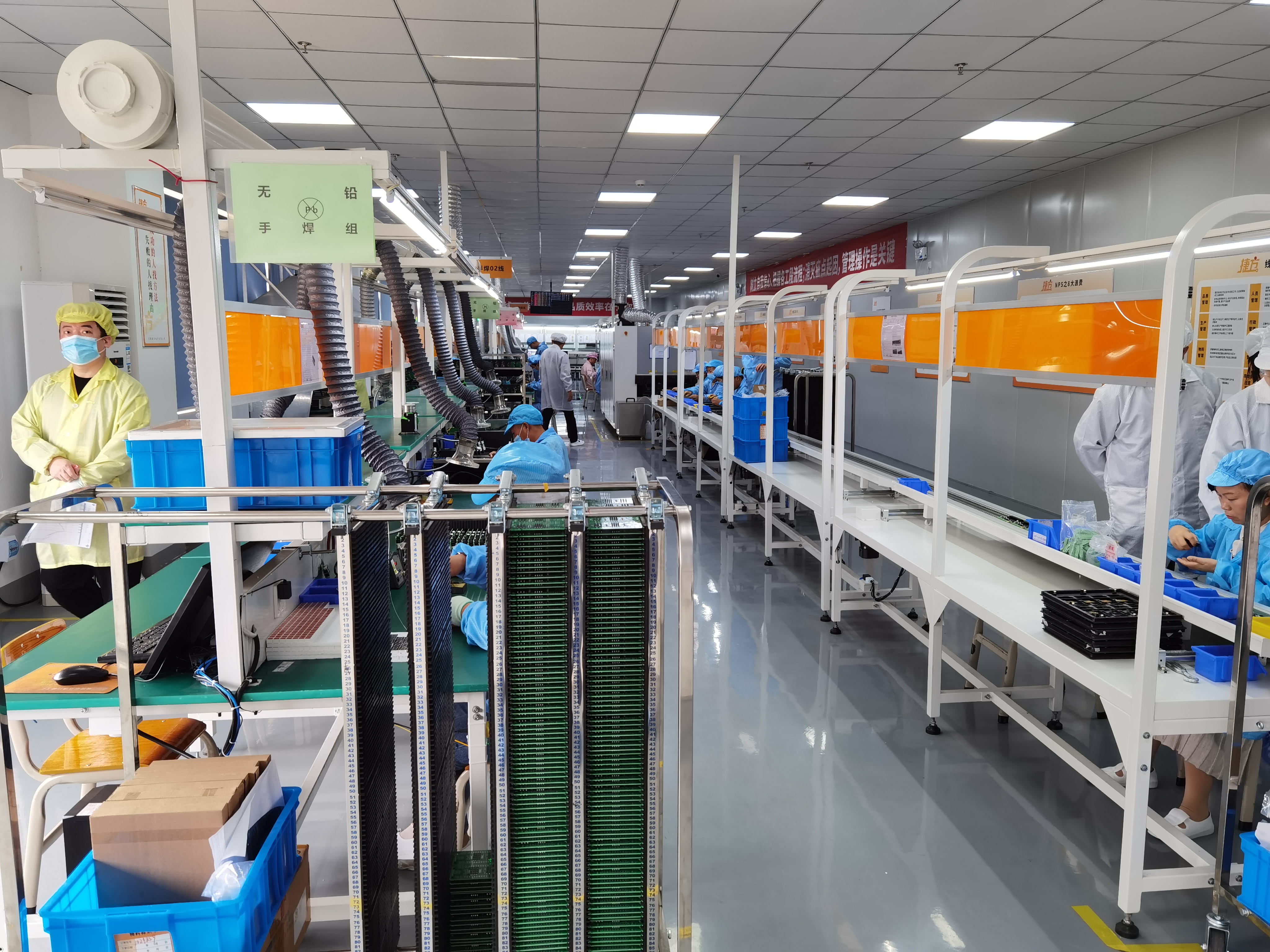

PCBA meaning electronics manufacturing describes the process of assembling electronic components onto a printed circuit board to create a functional device. PCBA stands for Printed Circuit Board Assembly. This process transforms a bare PCB into a working product. The global PCBA market size reached $68.4 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow to $105.8 billion by 2032. PCBA meaning electronics manufacturing highlights the difference between a PCB, which is only the board, and a PCBA, which includes all the mounted components. LTPCBA delivers PCBA services for customers who need reliable assembly solutions. PCBA enables smartphones, computers, and many other devices to work.
Key Takeaways
PCBA means assembling electronic parts onto a bare printed circuit board to make a working device.
The PCBA process includes placing components, soldering, and thorough inspection to ensure quality.
PCBA differs from PCB because PCB is just the bare board, while PCBA has all the parts attached and ready to function.
Two main assembly methods are Surface Mount Technology (SMT) for small, dense parts and Through-Hole Technology (THT) for stronger connections.
High-quality PCBA is vital for many industries like medical, automotive, and consumer electronics, ensuring devices work reliably and last longer.
PCBA Meaning in Electronics Manufacturing
What Is PCBA
PCBA meaning electronics manufacturing refers to the process of creating a functional electronic board by mounting and soldering components onto a printed circuit board. In electronics manufacturing, printed circuit board assembly transforms a bare PCB into a working circuit that powers devices like smartphones, computers, and medical equipment. The printed circuit board assembly process involves several steps, including component placement, soldering, and inspection, to ensure the board operates as intended.
Printed circuit board assembly stands as a core step in electronics production. The bare PCB, made from non-conductive materials such as FR4 or polyimide, contains copper tracks that form the electrical pathways. However, the board alone cannot perform any function. Only after the printed circuit board assembly process, when components like resistors, capacitors, and integrated circuits are attached, does the board become a PCBA. This distinction is fundamental in electronics manufacturing standards, as the PCBA is the finished product ready for integration into electronic devices.
A typical PCBA includes many essential components:
Inductors manage magnetic fields.
Diodes control current direction.
Transistors amplify or switch signals.
Integrated circuits handle complex processing.
Connectors link different parts of the device.
LEDs provide visual signals.
Each component plays a unique role in the printed circuit board assembly, ensuring the final PCBA can support and connect electronic circuits to achieve the desired electrical functions.
Printed Circuit Board Assembly Explained
Printed circuit board assembly, often called PCBA, involves several key steps that turn a simple board into a complex, functional system. The process starts with soldering components onto the PCB using methods like reflow soldering for surface-mount devices or wave soldering for through-hole parts. Automated machines place components with high precision, reducing errors and improving quality. After placement, the board goes through soldering, which secures each part and creates reliable electrical connections.
Inspection and testing follow the assembly stage. Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) checks for defects such as missing parts or solder bridges. X-ray inspection can reveal hidden issues in solder joints, especially in multilayer boards. These quality control steps ensure that each printed circuit board assembly meets strict standards for reliability and performance.
Printed circuit board assembly also includes protective measures. Manufacturers may apply coatings to shield the PCBA from moisture, dust, and other environmental factors. This step increases the durability and lifespan of the finished product.
The printed circuit board assembly process supports different types of boards:
Single-sided PCBA: Components on one side, used in simple devices.
Double-sided PCBA: Components on both sides, allowing more complex circuits.
Multilayer PCBA: Three or more layers, used in advanced electronics for higher performance.
Materials also vary. Flex PCBA uses flexible substrates for wearable or medical devices. Rigid PCBA uses solid boards for computers and cars. Rigid-flex PCBA combines both for specialized applications.
PCBA meaning electronics manufacturing highlights the importance of quality and reliability. LTPCBA, a leading provider in the field, uses advanced technology and strict inspection protocols to deliver high-quality printed circuit board assembly services. Their facility in Shenzhen features modern equipment and a skilled workforce. LTPCBA follows international standards, such as ISO and UL, and uses a 36-point inspection process, including AOI and X-ray checks, to ensure every PCBA meets or exceeds industry benchmarks.
Printed circuit board assembly enables electronic devices to perform their designated tasks. The process integrates many components, ensures precise connections, and provides the foundation for reliable, high-performance products. FPCBA, or flexible printed circuit board assembly, represents one of the specialized forms that support innovation in wearable and compact devices.
PCBA meaning electronics manufacturing goes beyond just building a board. It involves careful planning, advanced technology, and strict quality control to produce the functional heart of modern electronics. Companies like LTPCBA play a vital role in this process, supporting industries from consumer electronics to medical and automotive sectors.
PCB vs. PCBA
PCB Basics
A PCB, or Printed Circuit Board, forms the foundation of most electronic devices. In electronics manufacturing, a PCB consists of alternating layers of copper and insulating materials. The copper traces create electrical connections, while the board itself provides mechanical support for components. Manufacturers use materials like FR-4, Rogers, metal, and polyimide to fabricate PCBs. FR-4 is the most common due to its strength and low cost. The fabrication process includes etching copper layers, drilling holes, applying a solder mask, and adding silk screen labels. The result is a bare board with no electronic parts attached. This board undergoes electrical testing to ensure there are no faults before moving to the next stage.
A PCB acts as the structural platform for pcb assembly. It contains copper pads and traces that allow components to communicate and function together. The board itself cannot perform any electronic function until components are mounted during pcb assembly.
PCBA Differences
PCBA, or Printed Circuit Board Assembly, refers to the process of mounting and soldering electronic components onto a PCB. This step transforms the bare board into a functional electronic assembly. The pcb assembly process uses two main techniques: Surface-Mount Technology (SMT) and Thru-Hole Technology (THT). SMT involves applying solder paste, placing components with machines, and reflow soldering. THT requires drilling holes, inserting component leads, and soldering them in place. Each method includes inspection steps to ensure quality.
The differences between PCB and pcba become clear when comparing their roles and complexity:
Aspect | PCB (Printed Circuit Board) | PCBA (Printed Circuit Board Assembly) |
|---|---|---|
Definition | Bare, unpopulated board with copper traces and solder mask | Populated board with electronic components soldered in place |
Manufacturing | Fabrication involves etching copper layers and applying solder mask | Assembly involves placing and soldering components using SMT or thru-hole technology |
Components | None | Includes resistors, capacitors, ICs, and other electronic parts |
Testing | Basic electrical continuity and short circuit tests | Comprehensive functional and in-circuit testing |
Complexity | Simpler, foundational step | More complex due to component placement, soldering, and inspection |
Function | Provides mechanical support and electrical pathways | Performs the intended electronic function |
PCBA adds significant costs compared to producing a bare PCB. The assembly process includes the price of components, labor, testing, and quality assurance. Factors like assembly technique, component density, and design complexity influence the final cost. PCB production costs form only a part of the total pcba expense.
LTPCBA manages both PCB fabrication and pcb assembly under one roof. Their advanced facility in Shenzhen supports the entire process, from creating the bare board to completing the pcba. This integrated approach ensures high-quality results and reliable delivery for every pcb assembly project.
Tip: Understanding the difference between PCB and pcba helps engineers and students choose the right service for their electronic projects.
PCBA Assembly Process
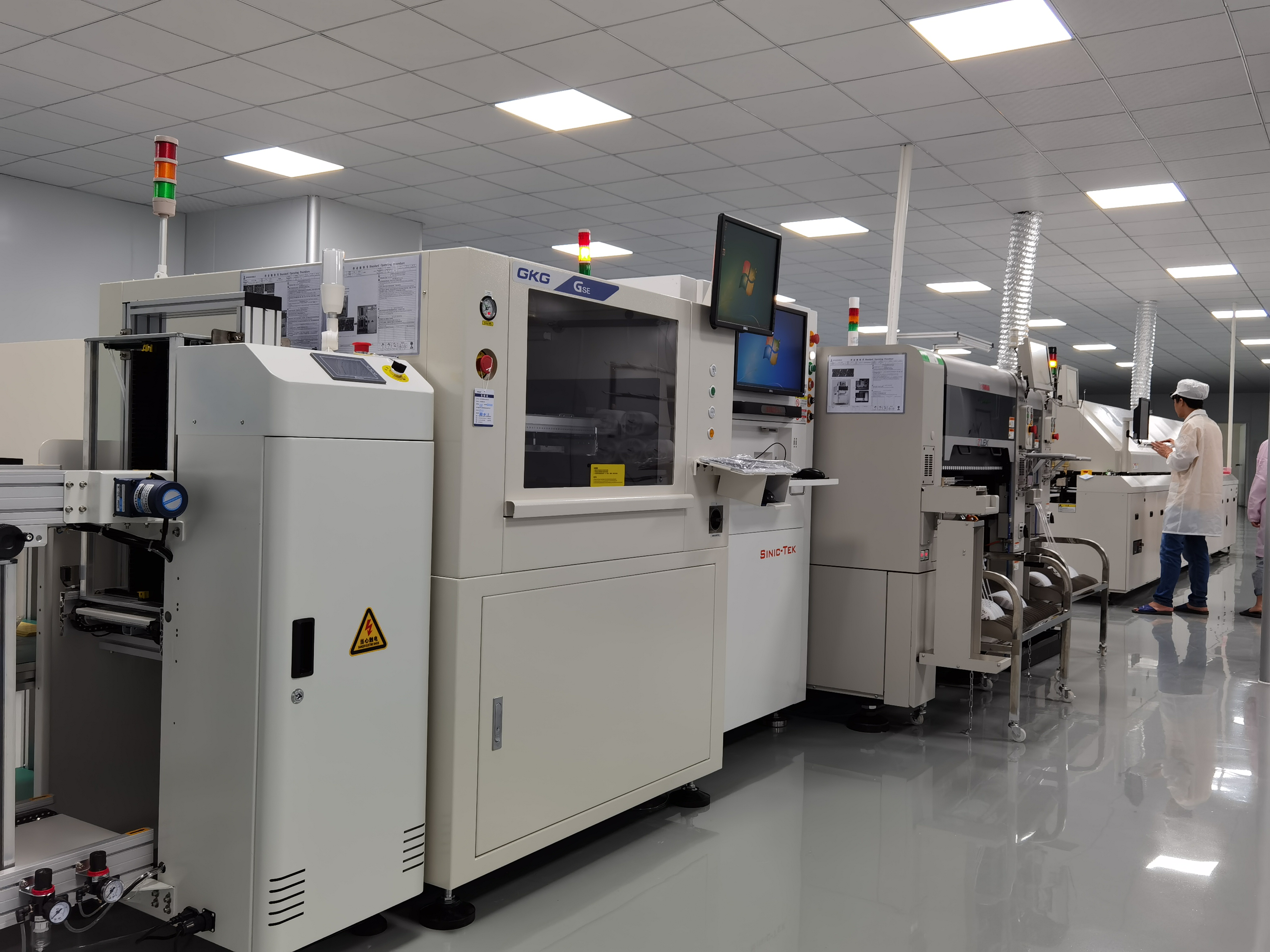

Main Steps
The pcba assembly process begins with careful preparation. Engineers first create prototypes to check manufacturability and follow design for manufacturing guidelines. They prepare a bill of materials and solder paste stencils for surface mount technology. Programming of assembly machines and adding test points for electrical checks come next. The main steps in the printed circuit board assembly process include:
Solder paste printing on the PCB pads using a stencil.
Automated pick and place machines position components on the board.
The board enters a reflow oven, where solder paste melts and secures the parts.
Inspection and quality control checks follow, using both manual and automated methods.
Through-hole components are inserted, either by hand or machine.
Wave soldering attaches these components to the board.
Final inspection and functional testing ensure the pcba works as intended.
Post-assembly cleaning removes any residues for reliability.
Each step in the pcb assembly process builds on the last, ensuring a reliable and high-quality printed circuit board assembly.
SMT and THT Methods
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) and Through-Hole Technology (THT) are the two main methods in the assembly process. More than 90% of modern printed circuit board assembly uses SMT. SMT places tiny components directly onto the board, allowing for high-density and compact designs. Automated machines handle most SMT tasks, making the pcb assembly process fast and precise.
THT, in contrast, involves inserting component leads into drilled holes. This method creates strong mechanical bonds and is still used for parts that need extra durability. THT is common in aerospace, military, and industrial pcba. The table below compares SMT and THT:
Aspect | SMT | THT |
|---|---|---|
Component Size | Very small | Larger |
PCB Density | High | Lower |
Assembly Process | Automated | More manual |
Mechanical Strength | Lower | Higher |
Suitability | High-volume, compact designs | Robust, low-volume builds |
Both SMT and THT play important roles in pcb assembly, depending on the needs of the printed circuit board assembly.
Quality Assurance at LTPCBA
LTPCBA uses advanced technology and strict standards throughout the assembly process. The company employs 3D Automated Optical Inspection with high-resolution cameras to check every pcb assembly for missing parts and solder issues. X-ray systems find hidden defects in complex boards. Solder Paste Inspection ensures correct paste volume and placement, preventing many common problems early in the process.
Statistical Process Control tracks key parameters like temperature and paste thickness, allowing engineers to fix issues before they affect the final product. First Article Inspection checks the first board in each batch with detailed tests. Final testing includes in-circuit and functional tests, as well as stress tests for harsh environments.
LTPCBA follows international standards such as ISO and IPC. The company uses an IoT-connected system for real-time monitoring and traceability. Manual inspections by skilled technicians add another layer of quality control. These steps ensure every pcb assembly meets the highest standards for printed circuit board assembly.
Importance and Applications
Why PCBA Matters
PCBA stands at the heart of modern electronics manufacturing. The assembly process transforms a simple board into a powerful, reliable device. PCBA enables manufacturers to create products that are smaller, faster, and more efficient. The use of automation and surface mount technology in pcb assembly increases production speed and reduces errors. This leads to higher reliability and lower costs for both manufacturers and consumers.
PCBA supports miniaturization by allowing more components to fit on a single board. Devices like smartphones, wearables, and medical implants rely on compact pcb assembly for their small size and advanced features. The assembly process also improves electrical performance and signal integrity, which means devices can run faster and use less energy. Rigorous testing and inspection during pcb assembly catch defects early, ensuring only high-quality products reach the market.
PCBA not only boosts efficiency but also supports environmental sustainability. Manufacturers use lead-free soldering and recycling practices to reduce waste and protect the environment.
The reliability of electronic devices depends on the quality of the pcba. Each stage of the assembly process demands strict standards. Automated equipment ensures precise placement and secure soldering of components. This careful approach reduces malfunctions and extends the life of the product.
Industry Uses
PCBA finds applications across many industries. Each sector depends on pcb assembly to deliver safe, reliable, and high-performing products.
Medical: PCBA powers implantable devices, diagnostic tools, and imaging equipment. High-density and flexible pcb assembly allow these devices to fit into small spaces and operate with precision.
Consumer Electronics: Smartphones, smartwatches, and fitness trackers all use advanced pcba for compact design and powerful features.
Automotive: Modern vehicles rely on pcb assembly for safety systems, infotainment, and electric vehicle controls. The automotive sector shows rapid growth, driven by new technologies and increased electronic content in cars.
Military and Aerospace: Defense and aircraft systems require robust pcba for reliability in harsh environments. Flexible and lightweight pcb assembly supports advanced designs.
Telecommunications and Industrial Control: Network equipment, industrial machines, and automation systems depend on pcba for fast, stable, and secure operation.
LTPCBA serves a wide range of industries with its comprehensive pcb assembly solutions. The company provides services for consumer electronics, healthcare, instrumentation, network communication, rail transit, industrial control, automation, machinery, and household appliances. LTPCBA follows strict quality standards, including ISO13485 and ISO9001, to meet the needs of each industry. Their advanced equipment and skilled team ensure every pcba meets high expectations for performance and reliability.
Industry | Example Applications |
|---|---|
Medical | Pacemakers, diagnostic devices |
Consumer Electronics | Smartphones, wearables |
Automotive | Safety systems, EV controls |
Military & Aerospace | Defense electronics, aircraft systems |
Telecommunications | Network devices, amplifiers |
Industrial Control | Automation, machinery equipment |
PCBA continues to drive innovation in every field. As technology advances, the demand for high-quality pcb assembly grows. Companies like LTPCBA help industries meet these challenges with reliable, efficient, and customized pcba solutions.
PCBA transforms a bare board into a functional electronic device by mounting and soldering components. This process bridges the gap between PCB fabrication and finished products, ensuring reliability and efficiency.
PCBA enables automation, high precision, and consistent quality.
PCB is the foundation, while PCBA delivers the complete, working assembly.
Choosing a provider like LTPCBA ensures strict quality control and advanced technology.
PCBA shapes the technology people use every day, from smartphones to cars.
FAQ
What does PCBA stand for?
PCBA stands for Printed Circuit Board Assembly. This term describes the process of mounting electronic components onto a printed circuit board to create a functional device.
How does PCBA differ from PCB?
A PCB is a bare board with copper traces. PCBA includes all the components soldered onto the PCB, making it a complete, working electronic assembly.
Which industries use PCBA services?
Many industries use PCBA, including medical, automotive, consumer electronics, aerospace, and industrial control. Each sector relies on PCBA for reliable and high-performance products.
What are SMT and THT in PCBA?
SMT means Surface Mount Technology. THT means Through-Hole Technology. SMT places components directly on the board. THT inserts component leads into holes for extra strength.
Why is quality assurance important in PCBA?
Quality assurance ensures every assembled board works correctly and lasts longer. Inspection methods like AOI and X-ray help detect defects early, improving reliability and safety.
See Also
Understanding The Meaning Of PCBA In Electronics
An Overview Of PCBA And Its Key Components
Sourcing Electronic Parts For Effective PCBA Production
