Key Factors That Influence PCBA Component Costs

Several factors drive component cost pcba in electronics manufacturing. The most significant influences on component cost pcba include material selection, assembly labor, and process complexity. The table below highlights the main categories and their specific impacts on component cost pcba:
Factor Category | Key Influences |
|---|---|
Component Costs | BOM Diversity, Brand & Package, Procurement Channels |
Assembly Labor & Process Costs | SMT and THT costs, Solder Paste & Flux pricing, Testing Processes |
Process Complexity & QC Requirements | Technical Difficulty, Quality Standards, Delivery Time |
Understanding these drivers of component cost pcba enables companies to better manage budgets, choose cost-effective solutions, and optimize their designs. LTPCBA leverages advanced technology and extensive industry expertise to provide efficient, affordable PCBA services while keeping component cost pcba in focus.
Key Takeaways
Material selection significantly impacts PCBA costs. Choose materials wisely to balance performance and budget.
Larger and more complex boards increase manufacturing costs. Opt for sizes that fit the application to control expenses.
Standard components are generally cheaper and easier to source than specialized parts. Use standard parts to avoid delays and reduce costs.
Material Choices

Impact on Component Cost PCBA
Material costs play a major role in determining the total price of a PCBA project. Different materials offer unique properties and price points. The most common materials include FR-4, aluminum, polyimide, and Rogers (PTFE). Each material affects material costs in a different way. For example, FR-4 is popular for its low material costs and good performance in general electronics. Aluminum offers better heat dissipation but increases material costs, especially in high-power applications. Polyimide and Rogers (PTFE) are used for specialized needs, such as flexible circuits or high-frequency devices, and their material costs are much higher.
Material | Description | Typical Applications | Price (Relative) | Performance Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
FR-4 | Fiberglass reinforced epoxy laminate | General-purpose electronics, consumer goods | Low to Medium | Good insulation, moderate thermal properties |
Aluminum | Metal core with high thermal conductivity | LED lighting, power electronics | Medium to High | Excellent heat dissipation, durable |
Polyimide | Flexible, high-temperature resistance | Aerospace, medical, automotive | High | Exceptional flexibility, high temperature |
Rogers (PTFE) | High-frequency, low dielectric loss | RF, radar, high-speed digital | High | Low signal loss at high frequencies |
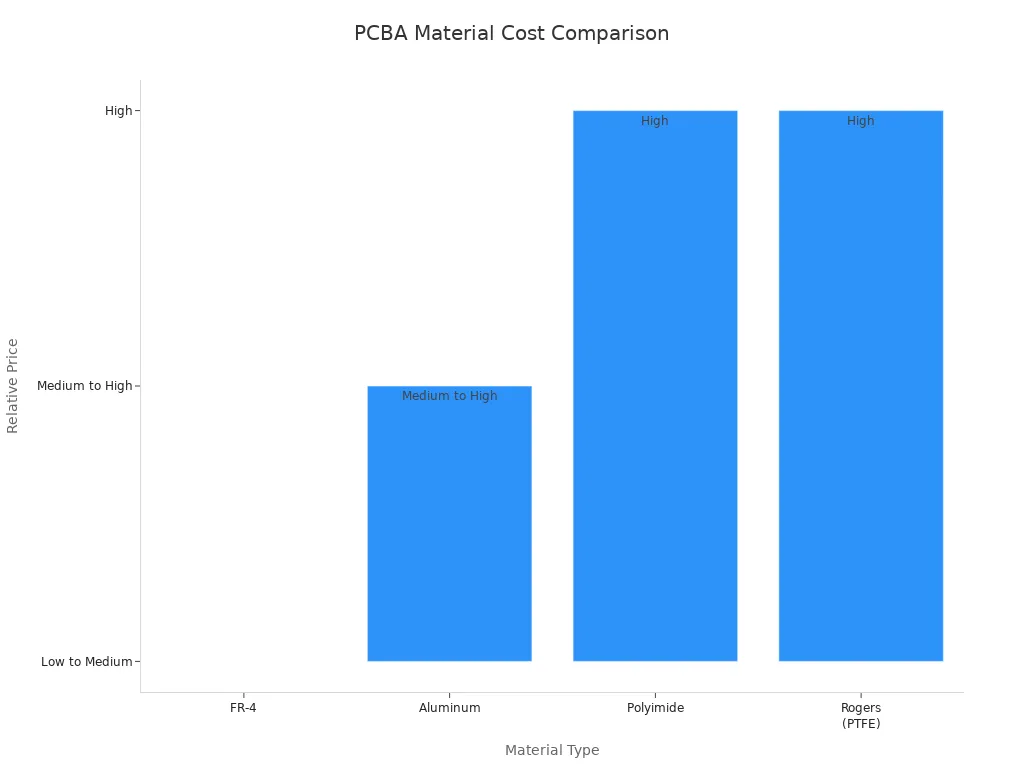
Manufacturers often choose FR-4 to keep material costs low for mass production. In contrast, high-performance materials like PTFE or ceramics raise material costs but deliver better results for advanced products. The choice of substrate directly impacts material costs, making it a key decision in every PCBA project.
LTPCBA’s Material Sourcing
LTPCBA uses several strategies to manage material costs while maintaining quality. The team starts with components that are easy to source, which helps control material costs and avoid delays. They use digital BOM tools for real-time updates, keeping material costs transparent. LTPCBA builds a preferred parts library, which speeds up sourcing and keeps material costs predictable. The company partners with suppliers who support rapid prototyping, further reducing material costs for new projects. LTPCBA also plans for substitutions, so if a part becomes scarce, they can switch quickly without raising material costs.
Compared to other providers, LTPCBA balances material costs and quality. The company works with mid-tier suppliers, offering value-added services and strong quality control. LTPCBA follows strict standards like ISO and IATF, using advanced testing to ensure high reliability. This approach keeps material costs reasonable while delivering dependable PCBA solutions.
Board Size & Layers
Size and Complexity
The size of a printed circuit board plays a major role in determining manufacturing costs. Larger boards require more materials and labor, which increases expenses. The complexity of the design also affects assembly time and cost. Complex printed circuit board layouts with high component density need precise assembly techniques and specialized equipment. These factors contribute to higher manufacturing costs and greater manufacturing complexity.
PCB Size | |
|---|---|
Small (2x2 to 4x4 inches) | $5 to $20 |
Medium (4x4 to 6x6 inches) | $10 to $30 |
Large (6x6 inches and above) | $20 to several hundred dollars |
Larger printed circuit boards not only use more substrate material but also demand more skilled labor during pcb manufacturing. Complex designs often require advanced processing, which raises manufacturing costs. High-density, multi-layered boards increase engineering and labor charges due to their intricate nature.
Tip: Choosing a board size that matches the application without excess can help control manufacturing costs and reduce unnecessary manufacturing complexity.
Layer Count
The number of layers in a printed circuit board directly impacts both material and assembly costs. As the number of layers increases, manufacturing complexity rises. Multilayer boards need advanced manufacturing techniques and specialized equipment, which leads to higher manufacturing costs.
More layers require additional substrate materials, copper foil, and insulation, increasing material costs.
Increased layer count means more processing steps like lamination, drilling, and alignment, which adds to manufacturing complexity.
Boards with a higher number of layers need advanced technology for proper signal transmission and alignment, raising manufacturing costs.
Multilayer printed circuit boards take longer to assemble and require skilled labor, further increasing expenses.
Manufacturers must balance the number of layers with performance needs and budget constraints. Careful planning during pcb manufacturing helps optimize costs and ensures reliable performance.
Component Type & Quantity
Standard vs. Specialized Parts
The choice between standard and specialized parts has a major impact on pcb manufacturing and assembly costs. Standard components are widely available and usually cost less. They help reduce procurement delays and keep projects on schedule. Specialized parts, such as high-value ICs or custom chips, often increase both procurement costs and lead times. These parts can also raise the overall cost of pcb manufacturing and assembly.
Standard components are less expensive than specialized parts.
Standard parts are easy to find, which helps avoid delays in pcb manufacturing and assembly.
Specialized components, like MCUs, GPUs, and FPGAs, can cost several dollars to hundreds of dollars each.
Component costs can make up more than 70% of the total cost in large-scale pcb manufacturing and assembly.
Selecting the right materials and components is essential for balancing performance and budget.
Volume and Cost Optimization
The quantity and production volume of an order play a key role in determining unit pricing and overall project costs. Larger orders benefit from economies of scale, which means the cost per unit drops as the order size increases. Bulk orders also allow for better packaging and shipping, further lowering expenses in pcb manufacturing and assembly.
The unit cost of PCBs decreases with larger order quantities.
Bulk orders help optimize packaging, reducing costs.
Prototype orders have higher per-unit costs due to setup fees and small batch sizes.
Production orders become more economical as quantity and production volume increase.
Per-Unit Cost Range (USD) | Typical Lead Time | |
|---|---|---|
Prototypes (5–10 units) | 50–200 | 1–5 business days |
Medium Runs (100–500 units) | 10–50 | 7–10 business days |
High-Volume (1,000+ units) | 2–20 | 14–20 business days |
Understanding how materials and components, as well as quantity and production volume, affect pricing helps companies plan more cost-effective pcb manufacturing and assembly projects.
Design Complexity
Factors That Influence Prices
Design complexity stands as one of the main factors that influence prices in PCBA projects. When engineers increase the number of layers or add more components to a board, the estimation of costs rises. Several factors affecting the cost include the type of assembly, such as Surface Mount Technology or Through-Hole Technology, and the density of components. Circuit complexity, with more placements and smaller parts, also drives up prices.
Other factors that influence prices include:
Board complexity, including the number of layers and component density
Variability in component prices due to specifications and sourcing
The type of assembly process used
The volume of assembly, which can lower prices for larger orders
Lead times and delivery options
Testing and compliance requirements
Labor and overhead costs
Flexible assemblies and special coatings can further increase prices. Each of these factors affecting the cost must be considered during estimation to avoid surprises later in the project.
LTPCBA’s Advanced Technology
LTPCBA uses advanced technology to manage complex designs and keep estimation accurate. The company employs high-speed pick-and-place machines with AI, which ensures precise placement and reduces errors. AI-driven inspection systems improve quality control and help maintain stable prices. Precision machinery, such as X-ray systems and robotic placement, supports high accuracy in assembly.
Technology Type | Description |
|---|---|
Automation | High-speed pick-and-place machines with AI for precise component placement |
AI-driven Systems | AI-powered inspection systems that enhance quality control and reduce defects |
Precision Machinery | X-ray systems and robotic placement for high accuracy |
3D Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) | Advanced cameras that detect errors with 99% accuracy |
These technologies allow LTPCBA to handle complex projects efficiently, keeping estimation reliable and helping customers control prices.
Surface Finish
Options and Cost Impact
Surface finish plays a key role in both the cost and performance of PCBA assemblies. Manufacturers select from several common finishes, each with unique properties and price points. The most widely used options include HASL, ENIG, OSP, Immersion Tin, Immersion Silver, and ENEPIG. The table below compares these finishes by cost, solderability, corrosion resistance, shelf life, and assembly compatibility:
Surface Finish | Cost | Solderability | Corrosion Resistance | Shelf Life | Assembly Compatibility |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
HASL | Low | Good | Moderate | Moderate, 12 mo | Conventional soldering processes |
ENIG | Moderate | Excellent | Excellent | Long, up to 24 mo | Lead-free soldering, wire bonding |
OSP | Low | Good | Moderate | Short, 6 mo | Lead-free soldering |
Immersion Tin | Moderate | Excellent | Moderate | Moderate, 12 mo | Lead-free soldering |
Immersion Silver | Moderate | Excellent | Moderate | Moderate, 12 mo | Lead-free soldering |
ENEPIG | High | Excellent | Excellent | Long, up to 24 mo | Lead-free soldering, wire bonding, mixed assembly |

The choice of surface finish affects both the initial cost and the long-term reliability of PCBA components. Premium finishes like ENIG and ENEPIG offer excellent solderability and corrosion resistance, which can extend shelf life and reduce the risk of failures. Lower-cost finishes such as HASL and OSP provide good performance for standard applications but may lead to higher rework costs if reliability becomes an issue.
Surface finish selection impacts protection against oxidation and corrosion.
Premium finishes enhance long-term reliability and storage stability.
Economical finishes may increase failure rates, raising rework costs.
Choosing the right finish helps balance performance, cost, and reliability.
Selecting the appropriate surface finish ensures that the assembly meets both technical and budget requirements.
Lead Time & Availability

Reduce PCB Manufacturing and Assembly Costs
Lead time and component availability play a big role in the total cost and timeline of a PCBA project. When a project needs a fast turnaround, costs often rise because suppliers may need to use express shipping or source parts from more expensive channels. Delays in sourcing critical components can extend project timelines and increase labor expenses. Supplier reliability and strong inventory management help keep projects on track and costs under control.
Factor | Impact on Timeline and Costs |
|---|---|
Supplier Reliability | Ensures timely delivery of components, reducing the risk of delays. |
Inventory Levels | Robust inventory management allows for quicker production times, minimizing delays. |
Component Selection | Choosing components with longer lead times can increase costs and extend project timelines. |
To reduce pcb manufacturing and assembly costs, companies can use several strategies:
Choose standard materials and components that are often in stock.
Simplify designs to avoid unnecessary complexity.
Use Design for Manufacturability (DFM) guidelines for easier assembly.
Work closely with reliable manufacturers who offer quick turnarounds.
LTPCBA’s Fast Turnaround
LTPCBA stands out for its fast turnaround and reliable delivery. The company offers typical turnaround times of 1-5 days for prototypes and mid-volume production. This speed matches or exceeds industry standards.
Provider | Typical Turnaround Times | Fast Turn PCB Availability | Production Range |
|---|---|---|---|
LTPCBA | 1-5 days | Yes | Prototype to mid-volume |
JLCPCB | 1-3 days | Yes | Prototype to high-volume |
MacroFab | 3-7 days | Yes | Prototype to production |
LTPCBA’s quick response service and 24-hour technical support help customers solve problems quickly. This support reduces the risk of delays and ensures projects stay on schedule. By planning ahead and working with LTPCBA, companies can manage lead times and keep costs predictable.
Testing & Quality
Quality Assurance at LTPCBA
LTPCBA places strong emphasis on quality throughout every stage of PCBA production. The company achieves a 99.5% pass rate on product delivery, reflecting its commitment to reliability and efficiency. Initial design validation ensures that each project starts with feasible and manufacturable designs. Final inspection and testing verify that every board functions as intended before shipment. Continuous monitoring of production metrics helps identify and address defects quickly.
Note: Implementing ISO and IPC standards, such as ISO 9001 and IPC-A-610, supports consistent quality management and reduces defects and rework costs.
LTPCBA uses several effective quality assurance processes:
Initial design validation to confirm manufacturability.
Final inspection and comprehensive testing before shipping.
Continuous monitoring of production metrics for defect reduction.
The company also focuses on simplicity in design, comprehensive testing protocols, and regular employee training. Data analysis helps LTPCBA identify trends and optimize processes for better quality. Design for Manufacturing reviews, careful material selection, and standardized process controls further enhance reliability.
Quality Assurance Process | Description |
|---|---|
Simplicity in Design | Simpler designs reduce errors during assembly. |
Comprehensive Testing Protocols | Thorough testing identifies defects early. |
Employee Training and Skill Development | Training improves awareness of potential defects. |
Continuous Improvement through Data Analysis | Data analysis finds trends and variations for optimization. |
Cost Optimization Strategies
Testing strategies play a major role in cost optimization for PCBA projects. During prototyping, flexible methods like flying probe tests and manual verification help adapt quickly to design changes and reduce costs. In mass production, automated optical inspection and in-circuit testing maximize first pass yield and minimize rework costs. High-reliability projects use advanced methods such as X-ray inspection and burn-in testing to ensure long-term performance.
LTPCBA applies several cost optimization strategies:
Define testing objectives to avoid over-testing and insufficient testing.
Use universal test hosts and modular designs to lower initial investment costs.
Analyze testing data to identify redundant tests and high-risk areas for optimization.
Engage in early design discussions to plan for testability and save costs on adjustments.
Implement phased testing strategies that adapt to product stability and production phases.
Tip: Early planning and phased testing help achieve cost optimization and maintain high quality standards.
Optimization of testing and quality assurance processes allows LTPCBA to deliver reliable products while controlling costs. These strategies ensure that customers receive dependable PCBA solutions with efficient cost optimization.
Project managers should review all key factors that affect the overall cost and production costs of PCBA. The table below shows how each cost factor contributes to the cost of pcb production and helps with cost estimation:
Cost Factor | Percentage of Total Cost | Description |
|---|---|---|
Raw Material Costs | 35-45% | Substrates and copper-clad laminates |
Layer Count | 25-35% | Lamination, drilling, and alignment |
Manufacturing Processes | 15-25% | Surface finishes and special processes |
Drill Costs | 5-10% | Via and hole drilling |
Tooling and Setup Costs | 5-10% | Masks and CNC programming |
Labor Costs | 5-15% | Skilled labor for fabrication and assembly |
Overhead and Margins | 5-10% | Facility and manufacturer margins |
Early consultation with LTPCBA supports cost estimation and reduces the overall cost of pcb production. The following strategies help lower production costs:
Cost-Saving Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
Reduced Overhead Costs | Focus on core strengths, lower unnecessary overhead |
Efficient Component Sourcing | Quick, affordable sourcing through global supply chain |
Minimized Rework Costs | Early testing and inspection prevent costly rework |
Streamlined Design Processes | Simplified supply chain, reduced coordination costs |
Early planning with LTPCBA ensures accurate cost estimation and helps control the cost of pcb production for every project.
FAQ
What factors most affect the price of pcb design and assembly?
Many factors impact the price, including board size, layer count, component type, and the quality of the pcb. The bill of materials also plays a key role.
How can companies achieve cost-effective materials selection in pcb design?
Engineers select cost-effective materials by comparing performance needs with price. They review supplier options and choose materials that support high-quality pcbs without raising costs.
Why does the price of pcb assembly change with design complexity?
Design complexity increases the price because more layers, components, and advanced features require extra steps. Complex pcb design often needs specialized equipment and skilled labor.
See Also
Understanding PCBA: Key Components and Their Functions
Sourcing Electronic Parts for Efficient PCBA Production
Essential Materials Required for Effective PCBA Manufacturing
