Heavy Copper PCB Assembly vs Standard PCB Assembly Key Differences
You notice the difference right away when you compare heavy copper pcb assembly to standard PCB assembly. The copper in heavy copper PCBs is much thicker, which lets you handle higher currents and better heat. See the main differences below:
Feature | Heavy Copper PCB | Standard PCB |
|---|---|---|
Copper Thickness | 4oz or more | 0.5oz–3oz |
Current Capacity | About 3A | |
Thermal Management | 30–50% more efficient | Standard |
Choosing the right PCB type helps you meet your project’s power and cooling needs.
Key Takeaways
Heavy copper PCBs have thicker copper layers (4 oz or more) compared to standard PCBs (0.5 oz to 3 oz), allowing them to handle higher currents and better heat dissipation.
Choosing the right PCB type is crucial for meeting your project's power and cooling needs. Heavy copper PCBs excel in high-power applications, while standard PCBs are suitable for everyday electronics.
Heavy copper PCBs provide improved thermal management, reducing operating temperatures and extending component life, making them ideal for demanding environments.
Overview
Standard PCB
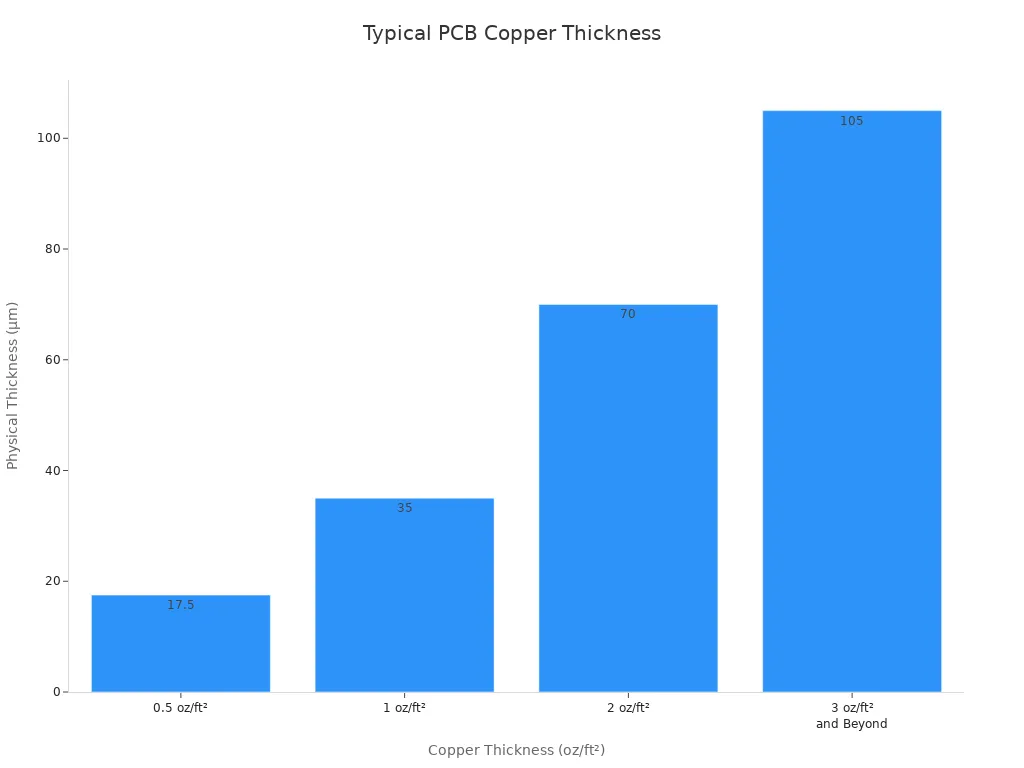
You often see standard PCBs in everyday electronics. These boards use copper layers that range from 0.5 oz/ft² to 3 oz/ft². The most common thickness is 1 oz/ft², which equals 35 micrometers. This thickness works well for devices like smartphones, computers, and automotive controls. Standard PCBs handle moderate currents and provide reliable performance for most consumer and industrial applications.
Copper Thickness (oz/ft²) | Physical Thickness (μm) | Applications |
|---|---|---|
0.5 oz/ft² | 17.5 μm | HDI boards, low power applications |
1 oz/ft² | 35 μm | Consumer electronics, automotive, industrial |
2 oz/ft² | 70 μm | Power supply boards, motor controllers |
3 oz/ft² and Beyond | > 105 μm | High-current power, power amplifiers |
Heavy Copper PCB
Heavy copper PCBs use copper layers that start at 4 oz/ft² and can go much higher. You choose these boards when your project needs to carry large currents or manage a lot of heat. Heavy copper PCBs work well in power electronics, industrial controls, and automotive systems that demand extra durability. The thick copper layers give these boards more strength and help them last longer in tough environments.
Key Features
Heavy copper PCBs stand out because of their mechanical strength and excellent thermal management. You get better heat dissipation and lower risk of circuit failure. These boards resist physical stress and reduce maintenance costs over time. Standard PCBs offer reliable performance for most uses, but heavy copper PCBs provide extra durability and reliability for demanding projects.
Tip: If your design needs to handle high power or harsh conditions, heavy copper PCBs give you the edge in durability and performance.
heavy copper pcb assembly vs standard
Copper Thickness
You see the most obvious difference between heavy copper pcb assembly and standard PCB assembly in copper thickness. Standard PCBs use copper layers from 1 oz to 3 oz. Heavy copper pcb assembly uses copper thickness from 4 oz to 10 oz, and sometimes even higher for extreme applications. This extra copper gives heavy copper circuit boards more strength and durability.
Type of PCB | Copper Thickness Range |
|---|---|
Standard PCB | 1 oz to 3 oz |
Heavy Copper PCB | 4 oz to 10 oz |
Thicker copper layers in heavy copper pcb assembly help you build boards that last longer and resist damage. You get better performance in tough environments. Heavy copper circuit boards also support more complex designs because you can add multiple copper layers.
Note: Copper thickness directly affects how much current and heat your board can handle. If your project needs high power density, heavy copper pcb assembly is the best choice.
Current Capacity
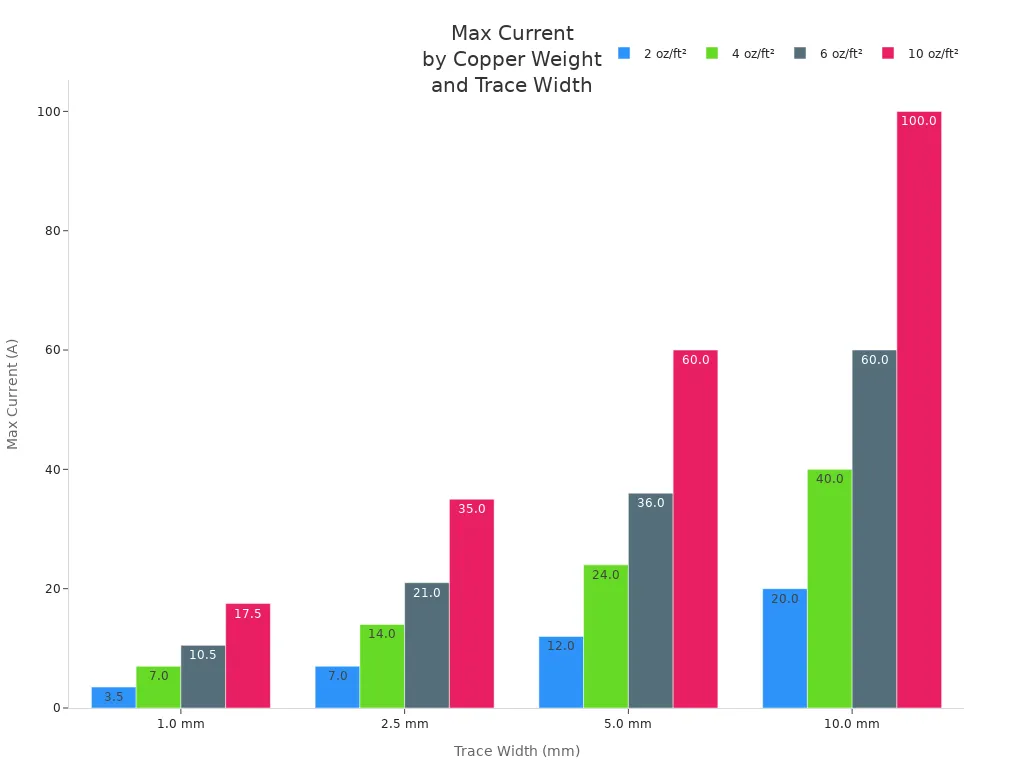
Heavy copper pcb assembly stands out for its current carrying capacity. Standard PCBs can handle about 3A per trace at 1 oz copper thickness. Heavy copper pcb assembly supports much higher currents, often up to 20A or more, depending on trace width and copper weight. For example, a 10 mm wide trace with 10 oz copper can carry up to 100A with only a small temperature rise.
Trace Width (mm) | 2 oz/ft² (A) | 4 oz/ft² (A) | 6 oz/ft² (A) | 10 oz/ft² (A) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1.0 | 3.5 | 7.0 | 10.5 | 17.5 |
2.5 | 7.0 | 14.0 | 21.0 | 35.0 |
5.0 | 12.0 | 24.0 | 36.0 | 60.0 |
10.0 | 20.0 | 40.0 | 60.0 | 100.0 |
Heavy copper pcb assembly lets you design boards for high power density and demanding industrial uses. You get lower resistance, better power distribution, and improved reliability. The current-carrying capacity of heavy copper circuit boards makes them ideal for power conversion, automotive, and motor control systems.
Thermal Management
Thermal management is another area where heavy copper pcb assembly excels. Standard PCBs have thermal resistance between 60°C/W and 80°C/W, with heat dissipation of 2–3 W/in². Heavy copper pcb assembly reduces thermal resistance to 15–35°C/W and boosts heat dissipation to 8–12 W/in².
PCB Type | Thermal Resistance (°C/W) | Heat Dissipation Capacity (W/in²) |
|---|---|---|
Standard PCBs | 60-80 | 2-3 |
Heavy Copper PCBs | 15-35 | 8-12 |
Heavy copper layers act as heat sinks, pulling heat away from critical components. You get lower operating temperatures and longer component life. Heavy copper pcb assembly can dissipate heat five times faster than standard designs. In motor controllers, you may see a temperature drop of 15–20°C, which extends the lifespan of your board by up to 40%.
Heavy copper pcb assembly provides better heat dissipation and reduces thermal stress.
You get more reliable performance in high-power and high-temperature environments.
Manufacturing Complexity
You face more challenges when you choose heavy copper pcb assembly. The thick copper layers require special manufacturing processes. Etching thick copper needs more time and careful control to avoid side etching and uneven copper thickness. Lamination uses multiple prepreg sheets and longer heating phases. Drilling through thick copper and substrates needs segmented drilling and adjusted parameters.
Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
Specialized Manufacturing Process | Requires higher copper foil pressure and longer deposition times for strong bonding. |
Multiple Copper Layers | Each layer needs its own deposition process, increasing complexity and time. |
Thicker Substrates | Thicker substrates are needed to support copper weight, affecting routing and drilling. |
Controlled Impedance | Requires precise control of copper thickness and layer spacing for high-speed signals. |
Uneven Electrodeposition | Longer deposition times can lead to uneven copper thickness. |
Warping | High copper weight can cause warping, leading to uneven thickness and assembly difficulties. |
Internal Connectivity | Plated through-holes can be difficult to manufacture, risking reliability. |
Delamination | Increased weight and thickness can cause delamination between layers and substrate. |
You need specialized equipment for heavy copper pcb assembly. Manufacturers use a mix of etching and electroplating to reach the required copper thickness. Thin traces become harder to produce, and thick traces may show unevenness. These challenges mean heavy copper pcb assembly takes more time and skill, but you get a board that performs better in demanding conditions.
Etching and plating processes must handle large amounts of copper.
Lamination and drilling require extra steps for thick boards.
Heavy copper pcb assembly supports copper thickness from 4 oz/ft² to 20 oz/ft², with extreme copper boards going even higher.
Tip: If your project needs high current carrying capacity, strong thermal management, and durability, heavy copper pcb assembly is the solution. You get a board that meets the toughest requirements.
Advantages & Limitations
Standard PCB Pros & Cons
You often choose standard PCBs for consumer electronics because they balance performance and cost. These boards support high-density integration and work well for high-speed signal transmission. You can rely on them for most everyday devices.
Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|
Mechanical strength problem | |
Reduced production costs | Increased processing difficulty |
Adapt to high-speed signal transmission | Electromagnetic compatibility challenges |
High-density integration capability | Higher manufacturing costs |
Long production cycle |
Note: Standard PCBs give you reliable performance for most applications, but you may face challenges with mechanical strength and electromagnetic compatibility in demanding environments.
heavy copper pcb Pros & Cons
When you need a board for high-power or industrial projects, heavy copper PCBs offer clear benefits. You get higher current capacity, excellent thermal management, and strong mechanical strength. These features make heavy copper boards ideal for automotive, industrial, and power electronics.
Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|
Higher current capacity | Higher costs |
Improved reliability and durability | Increased complexity in design and manufacturing |
Excellent thermal management | Potential performance issues (parasitic effects) |
Mechanical strength | Increased weight and size |
heavy copper PCBs handle higher current levels because of lower resistance and better heat dissipation.
You benefit from improved reliability since these boards withstand mechanical stress and reduce solder joint failures.
heavy copper boards protect against corrosion, oxidation, and moisture, which extends their lifespan.
You may notice that heavy copper PCBs increase costs and design complexity.
These boards can introduce performance issues like higher parasitic capacitance and inductance, and they may limit flexibility in circuit design.
Tip: Choose heavy copper PCBs when your project demands high power, durability, and superior heat management.
Applications

Standard PCB Uses
You see standard PCBs in many everyday products. These boards support a wide range of industries. You find them in devices that need reliable performance and moderate power handling. Here are the most common uses:
Consumer electronics such as smartphones and tablets
Medical industries for diagnostic equipment
Military applications including communication devices
Automotive industries for control modules
Aerospace and space exploration systems
Standard PCBs work well for products that require compact size and high-density integration. You benefit from cost-effective manufacturing and fast turnaround times. LTPCBA provides advanced assembly services for standard PCBs, ensuring quality and reliability for your projects.
Tip: Choose standard PCBs when you need efficient solutions for everyday electronics and industrial controls.
heavy copper pcb Uses
You select heavy copper PCBs for demanding environments and high-power applications. These boards excel in industries where durability and thermal management matter most. The table below shows where heavy copper PCBs make a difference:
Industry | Products |
|---|---|
Aerospace | EV Chargers |
Automotive | High Current Systems |
Medical | Power Storage Systems |
Networking/Communication | N/A |
Industrial | N/A |
Oil and Gas | N/A |
You rely on heavy copper PCBs for electric vehicle chargers, power storage, and high current systems. These boards handle extreme conditions and support advanced designs. LTPCBA specializes in heavy copper PCB assembly, using automated systems and strict quality standards to deliver robust solutions.
Note: Heavy copper PCBs give you the strength and reliability needed for power electronics, automotive, and aerospace projects.
Design & Manufacturing
Design Guidelines
When you design a heavy copper PCB, you must follow specific rules to ensure safety and performance. Start by making traces wide enough to handle the expected current. Use a temperature rise of 10°C to 20°C as your limit. For high-current paths, select vias with thicker copper plating, usually 2-3 mil, to prevent overheating. Request a thicker solder mask layer, about 1.5-2 mil, to protect the copper and avoid shorts. Balance copper across the board by adding dummy fills, which helps prevent warping. Work closely with your manufacturer to adjust trace spacing and avoid fine-pitch designs, since thick copper can make etching more difficult. Use heavy copper only where needed to control costs.
Manufacturing Process
The manufacturing process for heavy copper PCBs involves several extra steps compared to standard boards. You begin with material preparation, stacking multiple prepreg layers and copper foils to reach the desired thickness. Drilling and via formation require specialized equipment because of the increased depth. Copper plating and etching become more complex, as you need to deposit and shape thicker copper layers for high current. Surface finishing applies protective coatings to ensure the board resists environmental stress and remains easy to solder. Each step demands careful control to maintain quality and reliability.
LTPCBA Quality Assurance
You benefit from LTPCBA’s advanced technology and strict quality standards. The company uses automated optical inspection, X-ray systems, and high-speed pick-and-place machines to catch defects early. SMT first article inspection machines with AI help reduce errors. Reflow ovens with precise temperature control ensure strong solder joints. LTPCBA holds ISO 9001, IATF 16949, and UL certifications, which guarantee quality, safety, and compliance. These measures help you trust that your heavy copper PCB assembly will meet the highest industry standards.
Choosing the Right PCB
Project Needs
You should start by looking at your project’s main requirements. Each project has different needs, so matching the right PCB type is important. The table below helps you compare what to consider:
Project Requirement | Description |
|---|---|
Power Requirements | Assess the electrical load needed. |
Thermal Management Needs | Evaluate heat dissipation needs. |
Budget Constraints | Consider the financial limitations. |
Durability and Lifespan | Determine the expected longevity. |
If your design must handle high power or extreme heat, heavy copper boards offer better performance. For projects with tight budgets or standard power needs, standard PCBs may fit best.
Decision Tips
When you decide between heavy copper and standard PCB assembly, keep these tips in mind:
Heavy copper boards conduct heat away from components, which lowers failure rates.
They carry more current and survive repeated heating and cooling cycles.
You can use layered copper to make smaller PCBs without losing strength.
Heavy copper increases strength at connector sites, making your board more reliable.
Military, automotive, and industrial controls often use heavy copper for better heat management.
LTPCBA supports you through every step. You get help with certifications and compliance, plus a wide range of assembly and testing services. LTPCBA can handle both small and large production runs, so your project gets the right solution fast. Their team helps you define your needs, choose the right PCB type, and meet industry standards.
Tip: Reach out to LTPCBA’s experts for quick answers and technical support. You can trust their experience to guide you to the best PCB assembly for your project.
You see clear differences between heavy copper and standard PCB assembly. The table below highlights key factors:
Factor | Heavy Copper PCB Assembly | Standard PCB Assembly |
|---|---|---|
Copper Plating | Significant amounts | Lighter copper |
Design Complexity | More complex | Simpler |
Manufacturing | Challenging | Standard |
Understanding these differences helps you choose the right solution. LTPCBA offers expert support, cost savings, and improved reliability for your PCB projects.
FAQ
What is the main reason to choose heavy copper PCB assembly?
You choose heavy copper PCB assembly when your project needs to handle high current or extreme heat. This type gives you better durability and thermal management.
Can you use heavy copper PCBs for small devices?
You can use heavy copper PCBs in small devices, but you must consider size, weight, and cost. These boards work best in high-power or industrial applications.
Does LTPCBA support both standard and heavy copper PCB assembly?
Yes, LTPCBA offers assembly for both standard and heavy copper PCBs. You get expert support, advanced technology, and strict quality assurance for every project.
See Also
Evaluating Reliability: Through Hole PCB Versus SMT Assembly
Finding The Ideal Comprehensive Service For PCB Assembly
Choosing PCB Materials For Effective SMT Assembly Processes
When Traditional Through Hole PCB Assembly Beats SMT Technology
Determining The Right Turnkey PCB Assembly: Full Or Partial?
